Question
Question: Procambium forms - (a) Vascular cambium (b) Vascular tissues (c) Cork cambium (d) Intercalar...
Procambium forms -
(a) Vascular cambium
(b) Vascular tissues
(c) Cork cambium
(d) Intercalary meristem
Solution
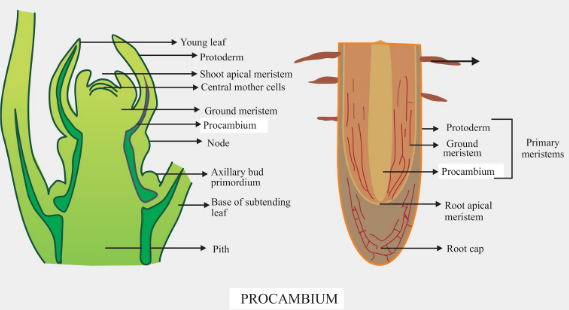
Procambium, as seen from the name, is a precursor to cambium which is a meristematic tissue. Meristematic tissues give rise to specific tissues depending on their location. It is also specific to either the root or the shoot.
Complete answer:
Vascular plants grow and develop through the growing parts of the plant that contain meristematic tissue.
- The procambium is a primary meristematic tissue that provides primary tissues, that include xylem and phloem, to the vascular system.
- It lies to the inner side of the protoderm and forms the epidermis.
- The other primary meristems are protoderm and ground meristem.
- Procambium gives rise to the vascular cambium, and cork cambium, secondary meristems.
- Vascular cambium is one of the secondary meristems. It produces secondary xylem and phloem. It is also responsible for the formation of wood in arboraceous plants.
- Cork cambium is also a secondary meristem. It gives rise to the periderm, which later replaces the epidermis.
- Intercalary meristems are present in angiosperm monocot plants. They are responsible for rapid stem elongation in bamboo and damaged leaf repair in grasses.
- The different types of meristems based on the location are apical (at the tips), intercalary (the middle), and lateral (at the sides).
So, the correct answer is ‘vascular tissues’.
Note:
Secondary meristems or lateral meristems surround the established stem of a plant and cause it to grow larger in diameter.
- Ground meristem is composed of parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells.
- There are a group of cells with stem cell function situated on the top of the meristem. They are known as the central zone.
