Question
Question: Potential difference across AB in the network shown in figure is 
A. 2V
B. 3V
C. 1V
D. 1.5V
Solution
Use the formula for equivalent resistance of the two resistors connected in series and parallel arrangement. Also use the expression for Ohm’s law. First determine the equivalent resistance in the circuit using the formula for equivalent resistance in parallel and series arrangement. Then determine the current in the circuit using Ohm’s law. Finally, calculate the potential difference across AB using Ohm’s law.
Formulae used:
The equivalent resistance Req of the two resistors R1 and R2 connected in parallel is
Req1=R11+R21 …… (1)
The equivalent resistance Req of the two resistors R1 and R2 connected in series is
Req=R1+R2 …… (2)
The expression for Ohm’s law is given by
V=IR …… (3)
Here, V is the potential difference between the two ends of the conductor, I is the current in the conductor and R is the resistance of the conductor.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
We have asked to calculate the potential difference between the ends A and B given in the circuit diagram.Let us first redraw the given circuit diagram to simplify the given circuit.
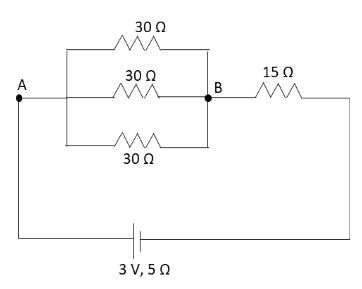
To calculate the potential difference between the ends A and B of the circuit, we need to calculate the net resistance and current in the circuit.Let us first determine the net resistance of three resistors connected in parallel.According to equation (1), we can write
R′1=30Ω1+30Ω1+30Ω1
⇒R′1=30Ω1+1+1
⇒R′=10Ω
Let us now calculate the equivalent resistance in the circuit using equation (2).
Req=10Ω+5Ω+15Ω
⇒Req=30Ω
Hence, the equivalent resistance in the circuit is 30Ω.
Let us now calculate the current in the circuit.Rewrite equation (3) for the potential difference across the circuit.
V=IReq
⇒I=ReqV
Substitute 3V for V and 30Ω for Req in the above equation.
⇒I=30Ω3V
⇒I=0.1A
Hence, the current through the circuit is 0.1A.
Now we can calculate the potential difference across AB.Rewrite equation (3) for the potential difference across AB.
VAB=IR′
Substitute 0.1A for I and 10Ω for R′ in the above equation.
VAB=(0.1A)(10Ω)
∴VAB=1V
Therefore, the potential difference across AB is 1V.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: The students may only determine the equivalent resistance of the three resistors connected in parallel and then use Ohm’s law to determine the current and then potential difference across AB. But this is an incorrect way to solve the question. The students should calculate the equivalent resistance in the whole circuit as the current flows the same through all resistors connected in series.
