Question
Question: Phosphoric acid is of great importance in the fertilizer production. Besides, phosphoric acid and it...
Phosphoric acid is of great importance in the fertilizer production. Besides, phosphoric acid and its various salts have a number of applications in metal treatment, food, detergent and toothpaste industries.
pKa=2.12,pKa=7.21,pKa=12.32
Small quantities of phosphoric acid are extensively used to impart sour or tart taste to many soft drinks such as colas and roots beers, in which a density of 1.00gmL−1 contains 0.05% by weight of phosphoric acid.
Phosphoric acid is used as a fertilizer for agriculture and an aqueous soil digesting micronutrient for plant growth. Plants can absorb zinc from water soluble only. In the given soil, zinc phosphate is only the source of zinc and phosphate ions. Ksp(zinc phosphate) = 9.1×10−33 .Phosphoric acid is a tribasic acid with three- step ionization constant. Thus, its structure is:
A. 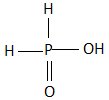
B. 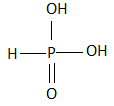
C. 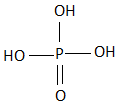
D. 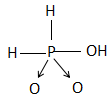
Solution
Phosphoric acid which is also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric (V) acid, is a weak acid with the chemical formula H3PO4 . It is normally found to be a colorless syrup of 85% concentration in water. The pure compound is a colorless solid. It is a tribasic acid and has the tendency to give 3 protons in aqueous solution.
Complete step by step answer:
All the three hydrogen atoms are acidic to varying degrees and can be lost from the molecule asH+ ions (protons). When all the threeH+ ions are removed, it results in the formation of an orthophosphate ion (PO43− ), commonly called as the phosphate ion. Removal of one or two protons gives dihydrogen phosphate ion H2PO42− , and the hydrogen phosphate ion HPO4− , respectively. Orthophosphoric acid also forms esters which are called as organophosphates. The structure of phosphoric acid is as follows:
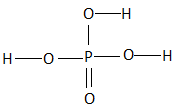
As we can see that, there are three hydroxyl groups attached to the phosphorus atom at the center and these hydrogen atoms undergo polarity due to the high electronegativity of the oxygen atom which helps in the easy loss of the protons from the acid.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Specific applications of phosphoric acid include:
(i) In anti-rust treatment by phosphate conversion coating or passivation.
(ii) As an external standard for phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance.
(iii) In phosphoric acid fuel cells.
(iv) In activated carbon production.
(v) In compound semiconductor processing, to etch Indium gallium arsenide selectively with respect to indium phosphide.
(vi) In microfabrication to etch silicon nitride selectively with respect to silicon dioxide.
(vii) As a pH adjuster in cosmetics and skin-care products.
(viii) As a sanitizing agent in the dairy, food, and brewing industries.
