Question
Question: Phenol on sulphonation at 100\(^{ o }{ C }\) gives: (a) o-phenol sulphonic acid (b) p-phenol sul...
Phenol on sulphonation at 100oC gives:
(a) o-phenol sulphonic acid
(b) p-phenol sulphonic acid
(c) m-phenol sulphonic acid
(d) o- and p-phenol sulphonic acid
Solution
The –OH group attached to the benzene ring in phenol is highly activating and is ortho and para directing. Sulphonation of phenol is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and is also reversible.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to solve this question we first need to understand the mechanism of sulphonation reaction.
The reaction is given below:
C6H5−OH100oCConc.H2SO4phenolsulphonicacid
Now we know that the –OH group attached to the benzene ring is highly activating and is ortho and para directing. The mechanism of sulphonation is as follows:
The first step involves the generation of the electrophile which is sulphur trioxide. It is generated by the acid-base equilibrium between two molecules of the sulphuric acid.
The reaction is shown below:
2H2SO4⇌SO3+HSO4−+H3O+
The second step involves the formation of the carbocation intermediate. The π electrons on the benzene ring in the phenol attack the sulphur trioxide molecules. This attack can take place either from the ortho position or the para position with respect to the –OH group present in the phenol. This is the slowest step and hence is also the rate determining step.
The reaction is shown below:
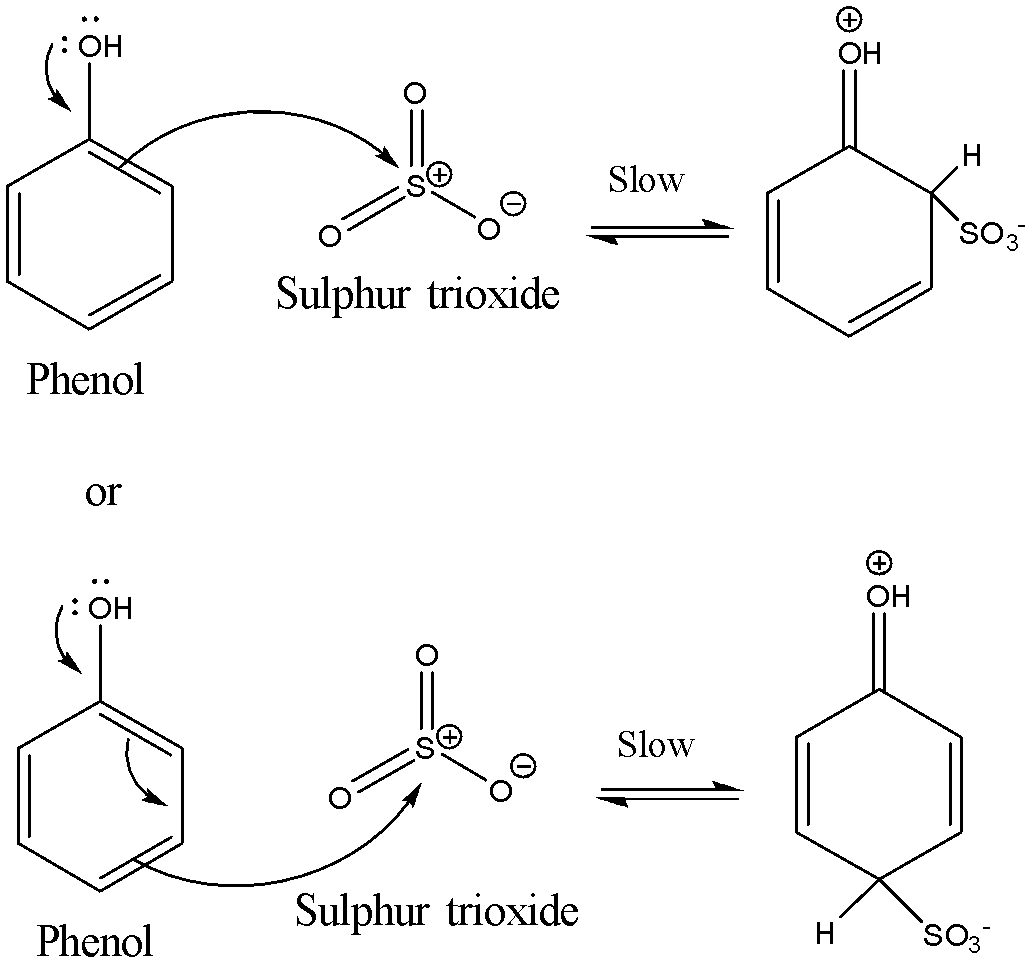
The third step involves the loss of a proton from the carbocation intermediate. It loses the proton to produce the sulphonic acid anion. The reaction is shown below:
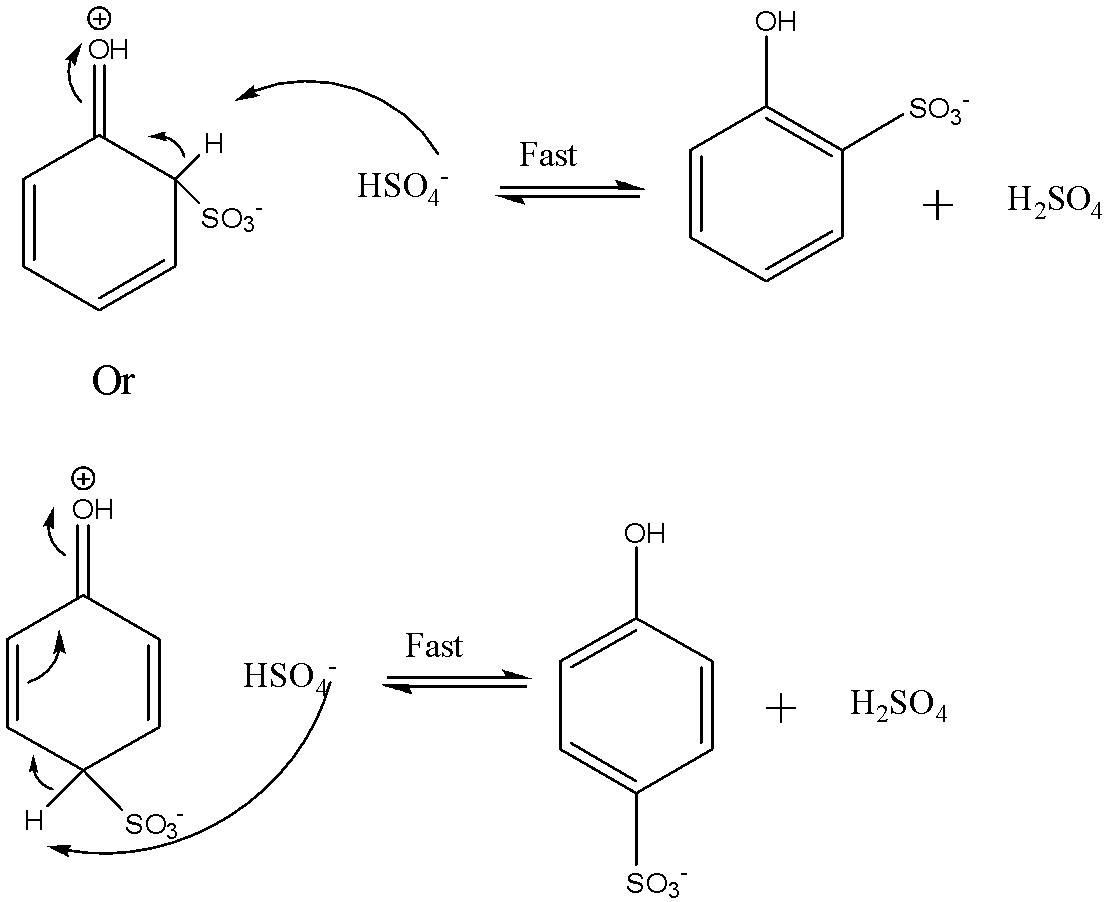
The final step involves the addition of proton to the phenol sulphonic acid anion to give the final product. The reaction is shown below:
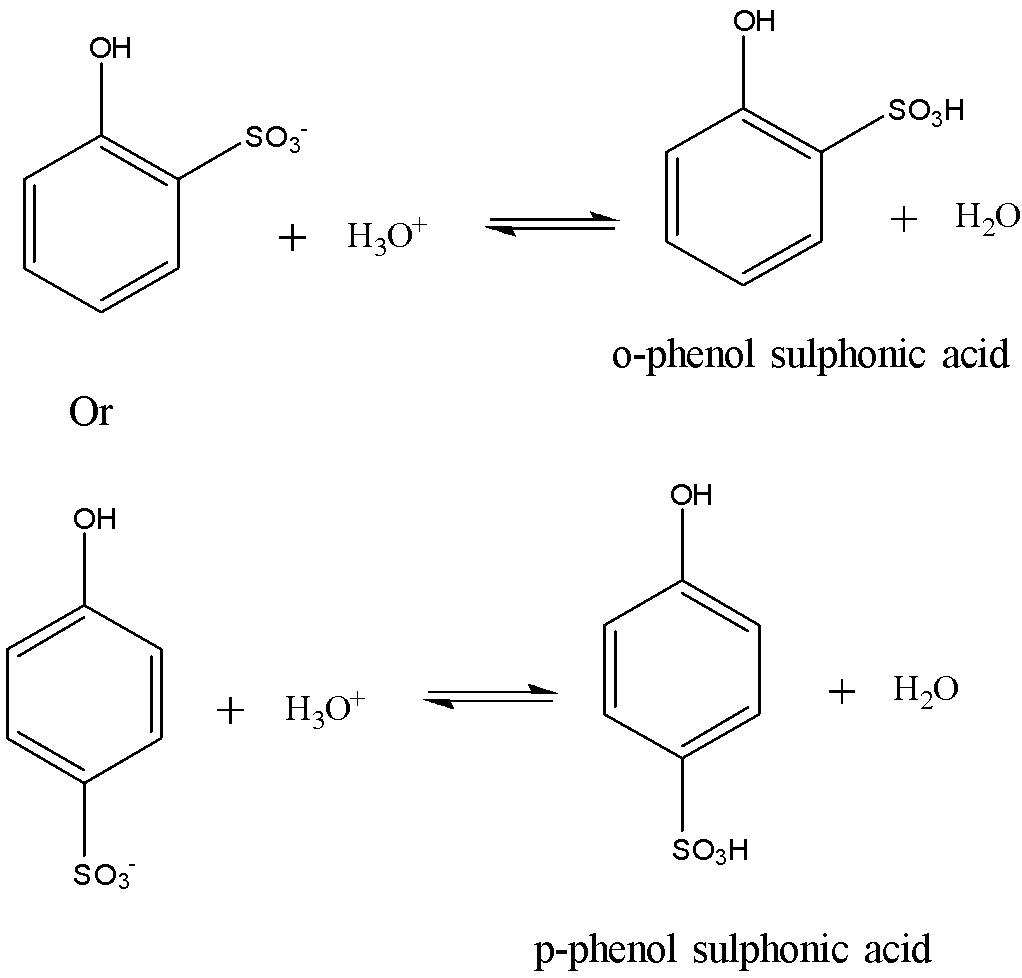
If the sulphonation of phenol is carried out at low temperatures such as at 288-293 K, then the kinetically controlled ortho isomer predominates. If the sulphonation is carried out at high temperatures such as at 373 K, then the thermodynamically controlled para-isomer predominates.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: If we heat the o-phenol sulphonic acid at 373K, then it will convert to the thermodynamically controlled p-phenol sulphonic acid product. This is mainly due to the reason that unlike other electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, sulphonation is reversible.
