Question
Question: Phenol on sulphonation at \({100^ \circ }C\) gives. A. O-phenol sulphonic acid. B. P-Phenol sulp...
Phenol on sulphonation at 100∘C gives.
A. O-phenol sulphonic acid.
B. P-Phenol sulphonic acid.
C. m-phenol sulphonic acid.
D. O-and P-phenol sulphonic acid.
Solution
We know that the reaction of phenol with conc. sulphuric acid is known as the sulphonation of phenol. The product of sulfonation depends upon the temperature.
Complete step by step answer: We must remember the hydroxyl group in a phenol molecule exhibits a robust activating effect on the benzene formula because it provides a ready source of electron density for the ring. This directing influence is so strong that you simply can often accomplish substitutions on phenols without the utilization of a catalyst.
Now, we see the sulphonation of phenol.
At low temperature, phenol reacts with o-phenol sulfonic acid. At low temperatures, the neighboring −OH group and group interact with one another. Hence ortho isomer predominates. We can write the chemical equation for the above reaction as,
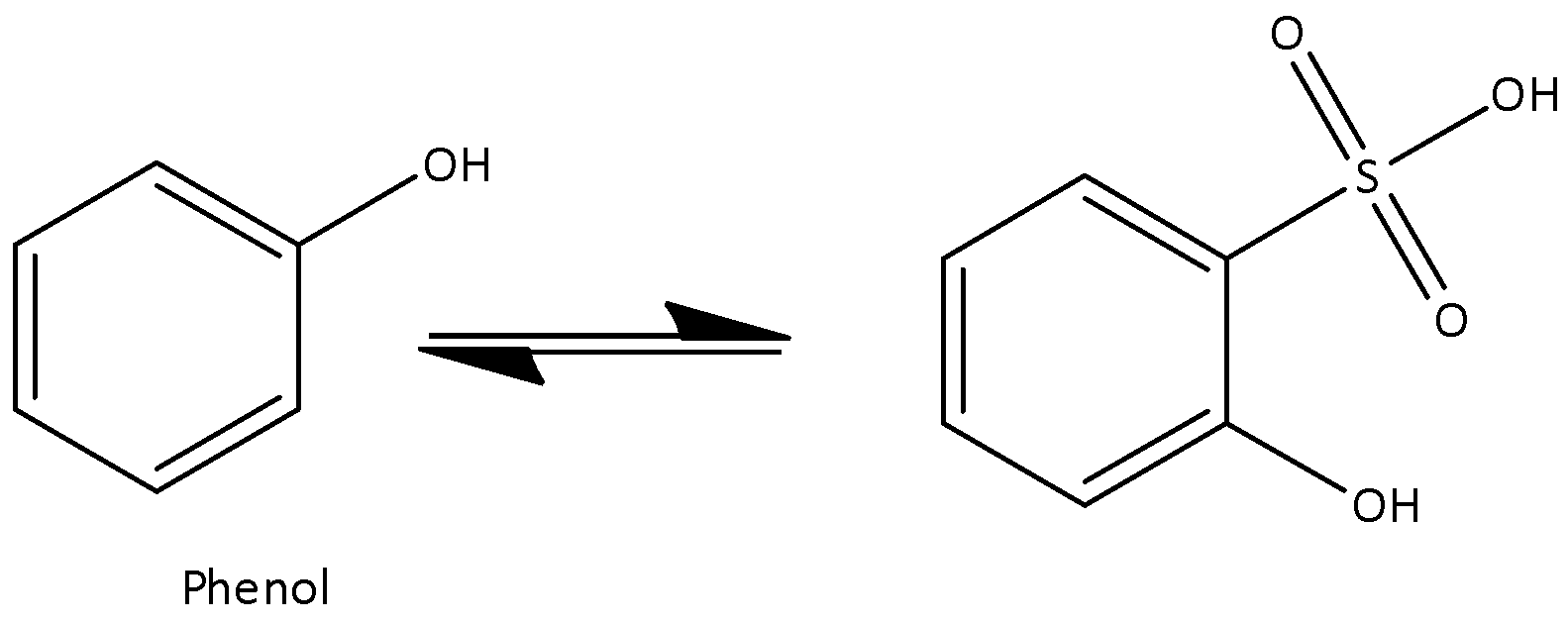
At high temperature, it's not possible to form any interaction and hence steric repulsion overcomes the attraction. Para-phenol sulfonic acid is obtained at high temperature. Now we can write the chemical equation for the above reaction as,
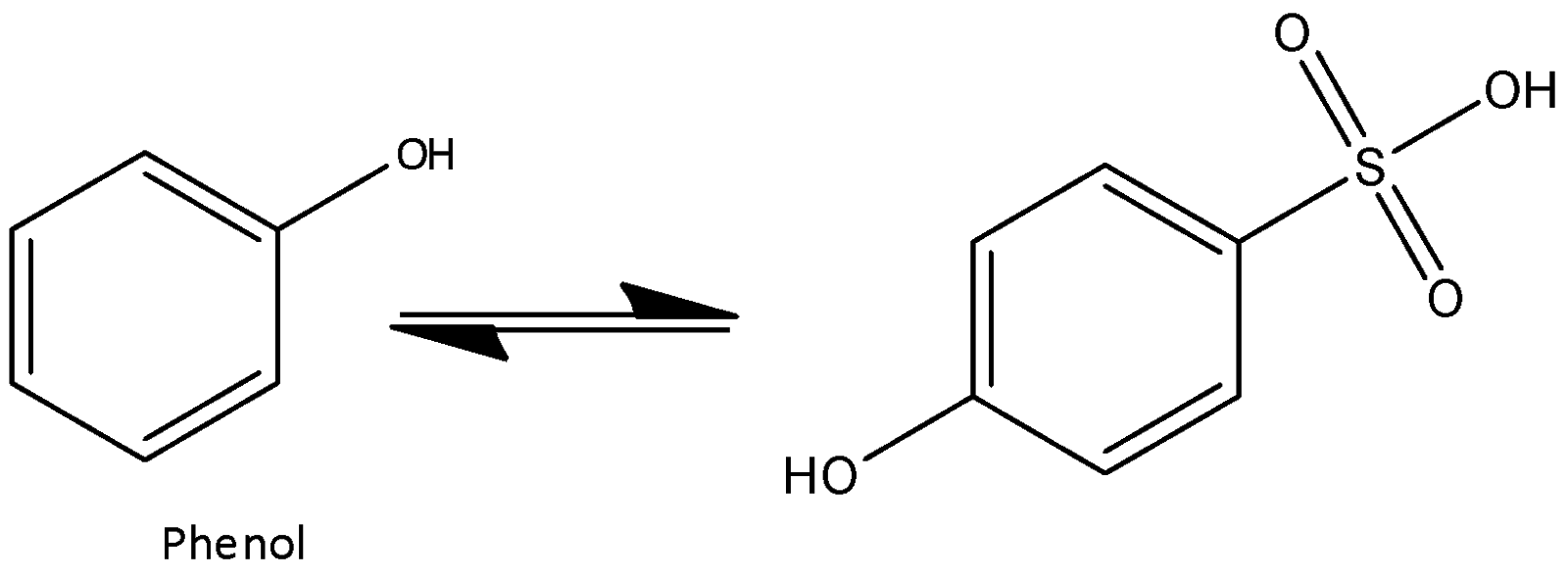
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We also remember an organic reaction in which an atom on an aromatic ring is replaced by a sulfonic acid in an electrophilic aromatic substitution is named aromatic sulfonation.
Now we can discuss the uses of sulphonic acid in our life.
-Aromatic sulfonic acids are used as detergents, dye, and drugs.
-Aromatic Sulfonic acids are intermediates in the preparation of dyes and many pharmaceuticals. -Sulphonation of anilines guide to a large group of sulfa drugs.
-Sulfonation of polystyrene is employed to form sodium polystyrene sulfonate, a standard natural process resin for water softening.
