Question
Question: Particle ‘A’ moves with speed \(10\,m/s\) in a frictionless circular fixed horizontal pipe of radius...
Particle ‘A’ moves with speed 10m/s in a frictionless circular fixed horizontal pipe of radius 5m and strikes with ‘B’ of double mass that of A. Coefficient of restitution is 21 and particle ‘A’ starts its journey at t=0. At what time will the second collision occur?
A. 2πs
B. 32πs
C. 25πs
D. 4πs
Solution
Coefficient of restitution is the ratio of final relative velocity and initial relative velocity between two objects after they collide.
Use conservation of momentum to determine velocity of particle ‘B’. Particle ‘A’ will come to rest after collision.
Use definition of speed to obtain time period for both collisions and then add to obtain time of second collision.
Formula used:
Time taken =magnitude of velocityDistance travelled
Complete step-by-step answer:
During any collision, the net momentum of the isolated system remains conserved. This is known as the law of conservation of momentum.
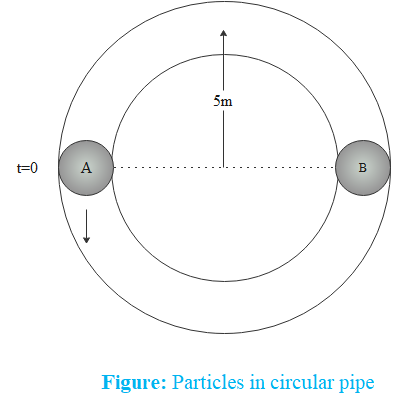
We are given that particle ‘A’ moves with speed 10m/s in a frictionless circular fixed horizontal pipe of radius 5m and strikes with ‘B’ of double mass that of A. Let us assume that the mass of particle ‘A’ is mA=m. Then the mass of particle ‘B’ will be mB=2m. The initial velocity of particle ‘B’ is vB=0. Then, initial momentum of the system is
pi=mava+mbvb
pi=m×10+2m×0=10m ….(1)
If vA′ and vB′ are the final velocity of particle ‘A’ and ‘B’ respectively, then final momentum of system is
pf=mAvA′+mBvB′=mvA′+2mvB′ ….(2)
By conservation of momentum, (1) equals (2):
10m=mvA′+2mvB′
⇒vA′+2vB′−10=0 ….(3)
Coefficient of restitution is the ratio of final relative velocity and initial relative velocity between two objects after they collide. It is denoted by e.
Here, e=21. So we can write
−e=vA−vBvA′−vB′=−21
Substituting the values and solving, we get
⇒21=10vA′−vB′
⇒vA′=−5+vB′ ….(4)
By substituting this value in (3), we get
−5+vB′+2vB′−10=3vB′−15=0
⇒vB′=5m/s
⇒vA′=0
After collision, A stops.
Initial time taken by A to hit B was
t1=velocitydistance travelled=10π×5=2πs
Time taken by B to hit A
t2=velocitydistance travelled=52π×5=2π
Time of second collision, t=t1+t2=2.5πs
Hence, option C is correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Law of conservation of linear momentum is applicable to elastic as well as inelastic collision.
In inelastic collision mechanical energy is not conserved. For perfectly inelastic collision coefficient of restitution is 0.
In a perfectly elastic collision, no kinetic energy is dissipated and therefore, the coefficient of restitution is 1.
