Question
Question: Oxidative phosphorylation of cytoplasmic \({\text{NADH}}\left( {{H^ + }} \right)\) takes place in ...
Oxidative phosphorylation of cytoplasmic NADH(H+) takes place in
(A) Cytosol
(B) E.R
(C) Mitochondria
(D) Golgi bodies
Solution
The oxidative phosphorylation of cytoplasmic NADH(H+) is the process in the electron transport chain that takes place in the eukaryotes. In this electron transport mechanism, the electrons are transported from the electron donors to the electron acceptors by the process of redox reactions.
Complete Answer:
NADH(H+) Ions are released from the products of the glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation and the Krebs’s cycle process.
- These ions help to undergo oxidative phosphorylation to convert the ADP into ATP (Adenosine triphosphate). 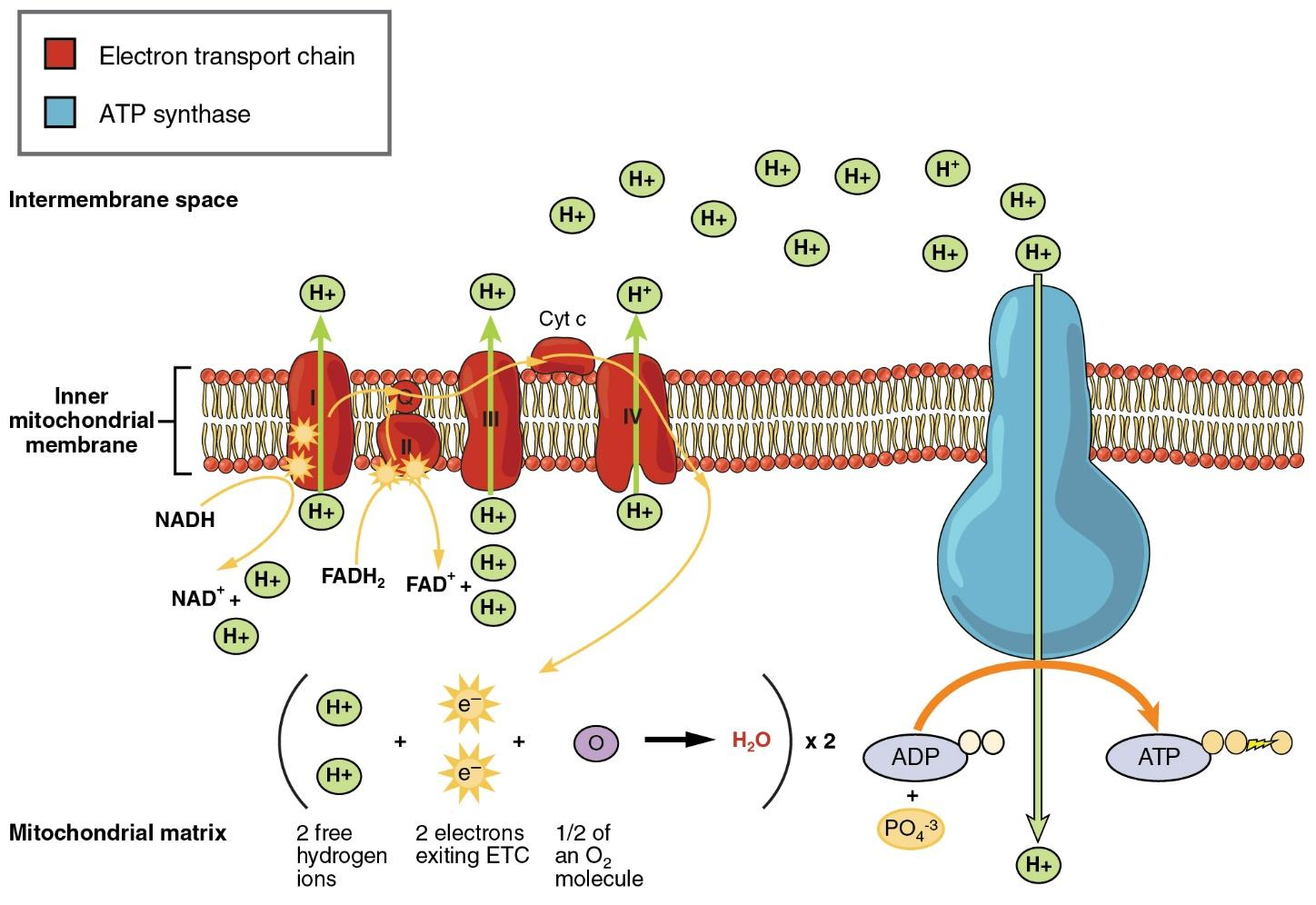
- The produced ATP synthase and electron transport assembly forms the integral part of the inner membrane of the mitochondria. This electron transport assembly helps in the catalyzation of the reactions of oxidation and reductions that take place simultaneously.
- In the electron transport chain, the electron donors pass the electron from them to the electronegative acceptor.
- The energy released in these transformations of electrons to oxygen helps to generate the proton gradient across the membrane of the mitochondria. This process pumps the proton to the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
- Hence phosphorylation of cytoplasmic NADH(H+) takes place in mitochondria.
Thus, the option (C) is correct.
Note: In the plants, the electron transport chain is known to take place in the thylakoid membrane. Here not NADH(H+) is involved, only the light energy is used to drive up the process of the redox reactions to convert ADP to the ATP.
