Question
Question: Ovule with funiculus lying close to micropyle is known as (a) Anatropous (b) Campylotropous ...
Ovule with funiculus lying close to micropyle is known as
(a) Anatropous
(b) Campylotropous
(c) Atropous
(d) Cytokinins
Solution
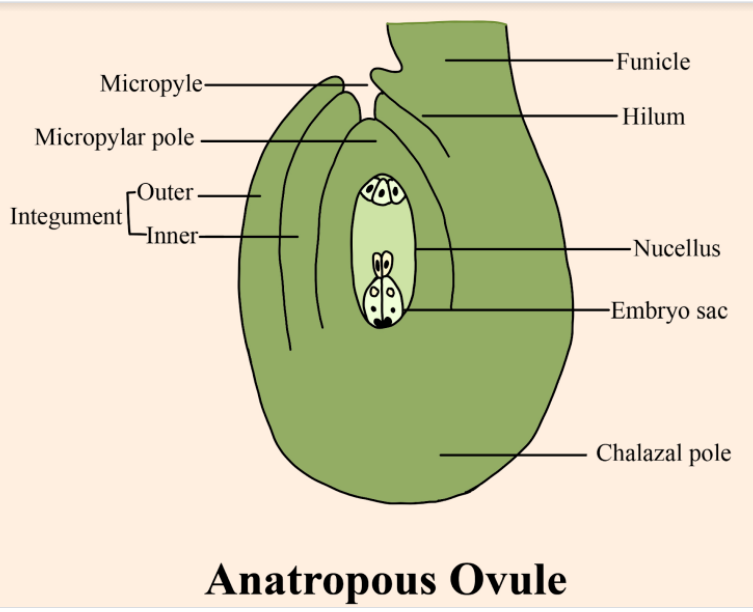
It is the most common type of ovule found in around 80% of angiosperm families. The egg cell turns 180 degrees and the micropyle enters the funiculus. Chalaza and micropyle are on the right, but the micropyle is bent 90 degrees towards the hilum.
Complete Answer:
The anatropous ovule is bent along the funicle so that the micropyle lies close to the hilum and chalazal end present at the other end. It is the most common type of ovule that is found in both monocots and dicots. Plants reproduce through sexual reproduction. Anther and Ovaries are the important male and female gametes of a plant respectively. Ovules are the megasporangium arising from the placenta of the ovary. The number of ovules in the ovary may be one or many.
Additional Information:
Structure of the ovule:
1. Funicle: It is the stalk of the ovule which attaches the ovule to the placenta of the ovary. It provides support and nutrition to the ovule.
2. Hilum: The point or a junction between the body of the ovule and the funicle is called the hilum.
3. Raphe: It is a longitudinal ridge that develops due to the fusion of the funicle with the body of the ovule longitudinally beyond the point of the hilum.
4. Integuments: These are the covering of the nucellus they are outer integuments and inner integuments. There may be only one integument or two integuments. This integument after fertilization becomes thick and hard.
5. Nucellus: Ovaries consist of diploid parenchymatous tissue called nucellus. Nucellus may be thick or thin. The Cells of the nucellus reserve the food materials.
6. Embryo sac: They are located inside the nucellus and contain female gametophytes.
7. Micropyle: The narrow opening present at the terminal end of the nucellus is called a micropyle.
8. Chalaza pole: It is the basal part of the nucellus from which integuments develop and is opposite to the micropyle.
So, the correct answer is, “Anatropous”
Note:
-In a campylotropous ovule, the ovule is bent hence the micropyle and chalaza do not lie in a straight line.
-In an orthotropic or anatropous ovule, the ovule is straight while the hilum, chalaza, and micropyle are straight.
-Cytokine is a plant hormone that divides cells.