Question
Question: Ordinary light incident on a glass slab at the polarizing angle suffers a deviation of \(22^\circ \)...
Ordinary light incident on a glass slab at the polarizing angle suffers a deviation of 22∘. Find the value of the angle of refraction.
A) 74∘
B) 22∘
C) 90∘
D) 34∘
Solution
The incident ordinary light will undergo refraction and reflection at the surface of the glass slab. The given deviation angle is the difference between the incident angle and the refracted angle. Here it is mentioned that the light is incident at the polarising angle. This suggests that the reflected light ray and the refracted light ray are perpendicular to each other.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Sketch a figure of the light incident on the glass slab.
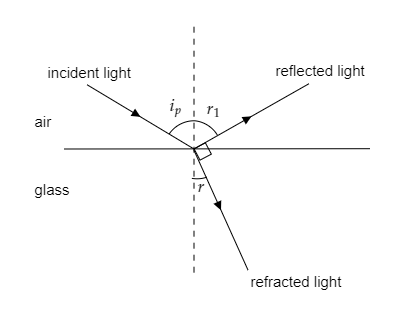
In the above figure, the dotted line represents the normal to the surface.
The angle of incidence is given to be the polarising angle so we have i=ip .
The angle of reflection is denoted by r1 and the angle of refraction is denoted by r in the figure.
The angle of deviation is given to be δ=ip−r=22∘ ------- (1).
Since i=ip, the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray will be 90∘ .
From the above figure, we have r+r1+90∘=180∘
⇒r+r1=90∘
The above expression can also be expressed as r+ip=90∘ ------- (2).
Step 2: Using equation (1) and (2) obtain the value of the angle of refraction.
Equation (1) is given as δ=ip−r=22∘ and equation (2) is given as r+ip=90∘ .
Subtracting left-hand side and right-hand side of equation (1) from that of equation (2) we get, r+ip−(ip−r)=90∘−22∘
⇒2r=68∘ or r=268∘=34∘
∴ the value of the angle of refraction is obtained to be r=34∘ .
So the correct option is D.
Note: A part of the incident ordinary light will undergo refraction as it enters from a rarer medium (air) to a denser medium (glass) and a part of it will undergo reflection at the surface of the glass slab. The laws of reflection suggest that the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal. So we replace the angle of reflection r1 by the angle of incidence ip to obtain equation (2).
