Question
Question: Order of basic strength between \[{{\text{N}}_{\text{P}}}\]and \[{{\mathbf{N}}_{\mathbf{Q}}}\]: 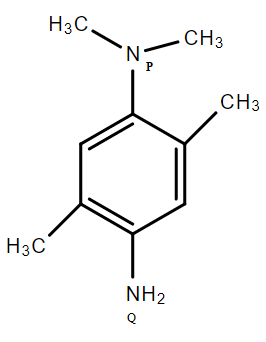
Solution
To answer this question, you should recall the concept of basicity of chemical compounds. Inductive Effect refers to the phenomenon wherein a permanent dipole arises in a given molecule due to the unequal sharing of the bonding electrons in the molecule. More the +I effect, more the basicity.
Complete step by step answer:
When an electron-releasing or an electron-withdrawing species is introduced to a chain of atoms, the corresponding negative or positive charge is relayed through the carbon chain by the atoms belonging to it. This causes a permanent dipole to arise in the molecule and is referred to as the inductive effect. Using the inductive effect, we can predict the acidity and basicity of compounds.
It can be said as a generalisation the electron-withdrawing groups increase the acidity of a compound and electron-donating groups decrease the acidity of a compound. The charge on a given atom and the charge on a group bonded to the atom play a strong part when determining the stability of the resulting molecule as per the inductive effect. An example of this can be observed when a group displaying the −I effect is bonded to a positively charged atom and the positive charge on the resulting molecule is amplified, reducing its stability. On the other hand, when a negatively charged atom is introduced to a group displaying an −I effect, the charge disparity is somewhat quenched and the resulting molecule would be stable as per the inductive effect.
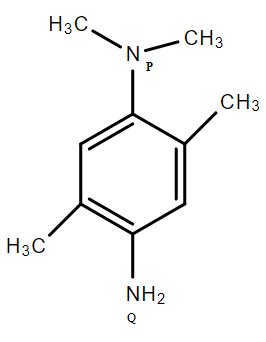
In this molecule, the electron-donating effect of the two CH3 molecules makes NP more basic.
Note: Make sure you remember the difference between different types of bases and acids.
Arrhenius Acid: Hydronium breaks up to yield a hydronium in solution. Arrhenius Base: Hydroxide is dissolved in water as OH−.
Bronsted-Lowry Acid: Hydronium is a H+ donor regardless of the solution. Bronsted-Lowry Base: > Hydroxide attacks and accepts them H+ form hydronium.
Lewis Acid: The H+ on Hydronium accepts the attacking electron pair to form a bond.
Lewis Base: Hydroxide donates electron pairs present over it to form a bond between itself and H+.
