Question
Question: Optical axis of a thin equi-convex lens is the X-axis. The coordinate of a point object and its imag...
Optical axis of a thin equi-convex lens is the X-axis. The coordinate of a point object and its images are (−20cm,1cm) and (25cm,−2cm) respectively
A. The lens is located at x=5cm
B. The lens is located at x=−5cm
C. The focal length of the lens is 10cm
D. The focal length of the lens is 15cm
Solution
A lens can be classified by the curvature of two optical surfaces. A lens is said to be a biconvex lens or double convex lens if both the surfaces of the lens are convex. An equi-convex lens is the lens in which surfaces of the lenses have the same radius of curvature.
Complete step by step answer:
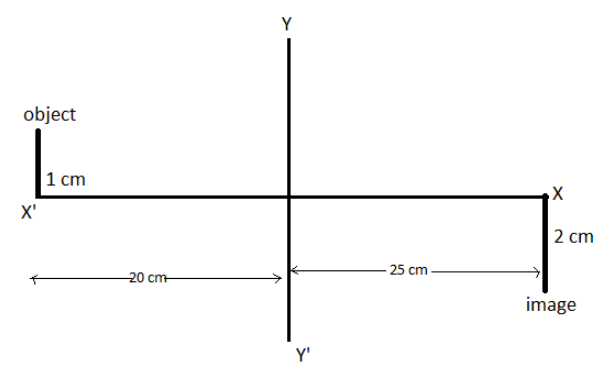
Now, it is given in the question, object and image is placed in x-y plane such that the coordinates of a point object and images are (−20cm,1cm) and (25cm,−2cm).
Therefore, we can say that, the distance of the object from the origin =25cm
Also, the distance of the image from the origin =−20cm
The size of the object =1cm
And, size of the image =−2cm
Therefore, the magnification is given by
m=uv
Where, v is the size of the image and u is the size of the object.
Therefore, by putting the values of v and u , we get
m=1−2
⇒m=−2
Now, negative sign here means that the image is real and inverted.
Now, for finding the position of lens, taking magnitude of v and u , we get
uv=2
∣v∣=2∣u∣
Now, adding ∣v∣ and ∣u∣ , we get
∣u∣+∣v∣= distance of object from the lens + distance of lens from the lens
∴u+2u=25−(−20)
⇒3u=25+20
⇒3u=45
⇒u=15
Therefore, the distance of the object from the lens is u=15cm
Now, distance of the image from the lens is ∣v∣=2∣u∣=30cm
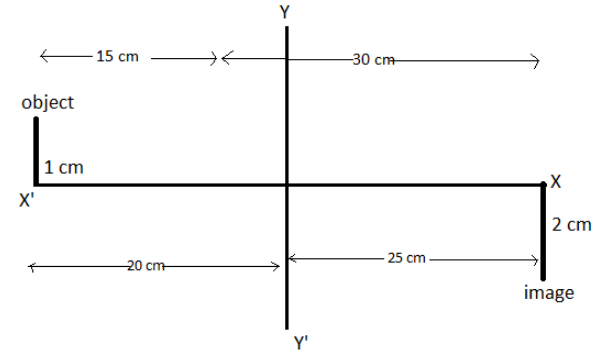
Therefore, the lens is placed at x=−5cm
Hence, option B is the correct option.
Note: Here, magnification is used to determine the nature of the image. Therefore, we got a real and inverted image. Real images are made by the converging rays where all the focus points are collected. An example of a real image is a cinema screen.
