Question
Question: On treatment of the following compound with a strong acid, the most susceptible site for bond cleava...
On treatment of the following compound with a strong acid, the most susceptible site for bond cleavage is:
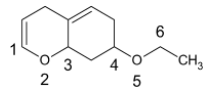
A. O2−C3
B. O5−C6
C. C4−O5
D. C1−O2
Solution
When treated with a strong acid, the given compound will undergo hydrolysis involving the cleavage of certain carbon oxygen bonds. That bond must be preferably cleaved which results into the formation of a stable carbocation.
Complete step by step solution:
In option A, considering the cleavage of O2−C3 bond.
We see that the carbocation formed on the C3 atom is a secondary carbocation. Furthermore, the positive charge on the carbon atom undergoes delocalization through the double bond present in the ring. This makes the carbocation stable.
For option B, considering the cleavage of O5−C6 bond.
When this bond is cleaved, it results in the formation of ethyl carbocation. The carbocation is primary and the only stabilization provided is by the electron donating inductive effect of the methyl group. We know that formation of a primary carbocation is not preferred
For option C, considering the cleavage of C4−O5 bond.
When this bond is cleaved, a secondary carbocation is formed. The positive charge is not in conjugation with the double bond. The only factors stabilizing the carbocation formed are inductive effects from the neighbouring carbon atoms.
For option D, considering the cleavage of C1−O2 bond.
When this bond is cleaved, a vinyl carbocation is formed. The carbon atom is sp2 hybridised and thus is more electronegative. This carbocation formed is unstable. As a result, we can say that the cleavage of this bond is not preferred.
Thus, we can conclude that cleavage of the O2−C3 bond yields the most stable carbocation and this bond is the most susceptible site for cleavage.
The correct option is A.
Note:
We know that the carbon atoms attached to the oxygen atoms are electrophilic in nature as the oxygen is highly electronegative.
When treated with a strong acid, the oxygen atom will be protonated and will tend to withdraw the electrons from the carbon oxygen bond resulting in the formation of a carbocation.
The carbocation thus formed must be stable in order for the cleavage to occur.
