Question
Question: On the horizontal surface of a truck \(\left( \mu =0.6 \right)\), a block of mass \(1kg\) is placed....
On the horizontal surface of a truck (μ=0.6), a block of mass 1kg is placed. If the truck is accelerating at the rate of 5 m/s2, then the frictional force on the block will be.
A. 5NB. 6NC. 5.88ND. 8N
Solution
Hint: The box is situated in a truck that is being accelerated. We know that objects in an accelerated frame of reference will experience a fictitious force acting on them. There is also a static frictional force present that acts on the block, which prevents the block from slipping. If the fictitious force is greater than the maximum frictional force, the object will start slipping in the other case the object will remain at the state of rest.
Complete step by step answer:
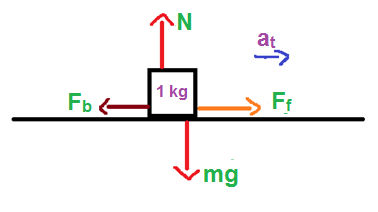
The block in the question has a mass of 1 kg, and it is placed on a truck whose surface has a coefficient of friction which is equal to μ=0.6. The truck starts moving with an acceleration of 5 m/s2since the truck is accelerating, the box will experience a pseudo opposite to the direction of acceleration of the truck. So, the pseudo force acting on the block can be written as,
Fb=m×at
Where
m is the mass of the block.
at is the acceleration of the truck.
So, we can substitute the values of mass and acceleration in the above equation,
Fb=(1kg)×(5m/s2)
Fb=5 N … equation (1)
So the fictitious acting on the block is 5 N.
Next, we have to find out the max frictional force that can act on the block. Which is given by the equation,
Ff=μN
From the figure, it is clear that N=mg.
So we write the force of friction as,
Ff=μ(mg)
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get,
Ff=(0.6)×(1kg×9.8m/s2)
∴Ff=5.88N … equation (2)
So, from equation (1) and (2), it is clear that the maximum frictional force is greater than the fictitious force acting on the block. This implies that the object will remain at rest and will have a force acting on it equal to the pseudo force.
So, the force acting on the block will be 5 N.
So, the answer to the question is the option (A).
Note:
Fictitious forces are also called pseudo force which is produced due to the accelerated frame of reference and not due to any contact force. For a system or frame of reference moving with a constant velocity, pseudo forces will not be present.
Coriolis Force and centrifugal force are two examples of pseudo forces acting on a body in a rotating frame of reference. In rotational motion, even if the body is moving with a constant velocity, it has an acceleration due to change in the direction of the velocity of the object when the object is revolving around a circle with constant speed. We call this type of circular motion as uniform circular motion.
