Question
Question: On the basis of Werner’s theory explain, why cobalt ammine complex, \( CoC{l_3}4N{H_3} \) when treat...
On the basis of Werner’s theory explain, why cobalt ammine complex, CoCl34NH3 when treated with AgNO3 solution precipitates only one Cl− ion even though there are three Cl− ions?
Solution
In complex compounds, the central metal atom shows two types of valency. They are primary valency and secondary valency. The primary valency relates to the oxidation state and the secondary valency relates to the coordination number. The coordination number or secondary valency is fixed for a metal atom.
Complete answer:
Complex compounds are also known as coordination compounds. In these compounds, the ions or molecules present cannot give the test. As these are the compounds that can retain their identity even dissolved in water or any other organic solvents.
A complex compound consists of a central metal atom and ligands. According to Werner’s theory, the central metal atom in complex compounds shows two types of valances. They are primary valency and secondary valency.
The primary valency can be satisfied by the oxidation number whereas the secondary valency can be satisfied by the coordination number.
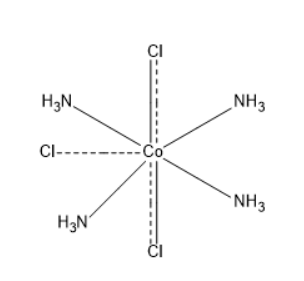
In CoCl34NH3 , two chlorine ligands show both the primary valency and secondary valency. The remaining one chlorine shows only secondary valency. Thus, only this one chlorine can be precipitated when the given complex is mixed with AgNO3 .
Note:
The primary valency was represented by the black continuous line in complex compounds, whereas the secondary valency can be represented by the dotted lines. The ligands which were showing only secondary valency can be precipitated when mixed with reagents like silver nitrate.
