Question
Question: On the addition of which compound the reaction will proceed in the forward direction? \([B{(OH)_3}...
On the addition of which compound the reaction will proceed in the forward direction?
[B(OH)3+NaOH→Na[B(OH)4] (aq)]
A) Cis−1,2−diol
B) Trans−1,2−diol
C) Borax
D) Na2HPO4
Solution
This reaction will be considered as a reversible reaction because when sodium metaborate Na[B(OH4)] is formed by the reaction between B(OH)3 and NaOH takes place. This sodium metaborate gets hydrolyzed and moves the reaction in the backward direction thereby regenerating B(OH)3 and NaOH .
The backward reaction is given as:
Na[B(OH)4]→NaOH+B(OH)3 (on hydrolysis)
Complete solution:
If we add certain organic polyhydroxy compounds such as glycerol, Cis−1,2−diol , catechol, mannitol or sugars to the reaction mixture, then B(OH)3 will act as a strong monobasic acid and will further combine with polyhydroxy compounds to give chelated complex compound. The chelated complex compound formed will increase the stability of the complex and due to this higher stability, the reaction will proceed in the forward direction.
So, the added compound must be Cis−1,2−diol to enhance the properties of the acid present. It will thus form a very stable complex with [B(OH)4]− thereby removing it from the solution. We already know that the reaction is a reversible reaction and so on the removal of this chelated complex formed, will shift the reaction in the forward direction. And thus all the B(OH)3 present in the reaction mixture will react with NaOH which also means that it will behave as a strong acid in the presence of Cis−1,2−diol.
The chelated complex formed is:
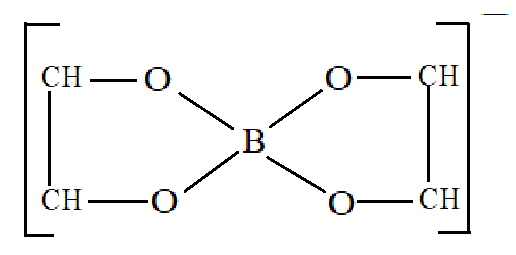
Therefore, from the above explanation we can say that the correct option is (A).
Note: We know that a chelate complex is a structure which is formed when a central metal atom binds with large molecules known as ligands in a cyclic or ring structure. Chelate complexes are more stable because they contain multidentate ligands which are more stable than unidentate ligands. Multidentate ligands are more stable because they can displace more than one molecule of water.
