Question
Question: On mixing 10 ml of acetone with 40 ml of chloroform the total volume of the solution is: A) < 50 m...
On mixing 10 ml of acetone with 40 ml of chloroform the total volume of the solution is:
A) < 50 ml
B) > 50 ml
C) = 50 ml
D) can not be predicted
Solution
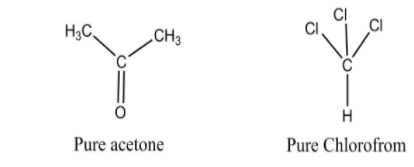
Acetone (CH3COCH3) is a keto compound. The carbon atom of the carbonyl group (⟩C=O) in sp2 hybridized. On the other hand, chloroform (CHCl3) is a substituted product of methane & the central carbon atom is sp3 hybridized here. Both are organic compounds.
Complete answer:
To solve this question, we have to know about the following things:
Volume of mixing: when two miscible compounds are mixed, the volume of the resulting solution is always different from the sum of the volume of the components mixed. This change in volume of the solution is called the volume of mixing . It happens because all the solutions in practice are non-ideal solutions.
Neither pure acetone nor pure chloroform can form intermolecular H-bond.
Mixture of chloroform & acetone forms intermolecular H-bond.
The mixture solution shows negative deviation from Raoult’s law, i.e., it is a non-ideal solution.
When we are mixing the two compounds H-bonding occurs between the H-atom and an electronegative atom, mainly O, N or F atom. The structure of pure acetone (CH3COCH3) or pure chloroform (CHCl3) are incapable of forming H-bonding.
But when these two are mixed the O atom of acetone forms H-bond with the H atom of chloroform.
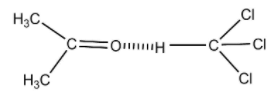
H- bonding in the solution
Thus, by the formation of intermolecular H-bond, the intermolecular attraction is increased in the solution than that of pure components. This increased intermolecular attraction reduces their intermolecular spaces & the molecules are more tightly held in the solution. Therefore, the volume of mixing (ΔVmix) becomes negative, i.e., the volume of the solution is less than the sum of the volume of acetone (10ml) & chloroform (40ml) added.
Thus, the correct answer is (A) <50 ml.
Note: Remember, that all the solutions are non-ideal in practical. So, the volume of mixing (ΔVmix) is always either negative (in case of increased attraction among the molecular) or positive (in case of decreased attraction among the molecular).
∴Vmix=O [ always for a non-ideal solution].
You need to know whether any intermolecular attractive forces are present or not in the solution.
