Question
Question: Number of possible isomers for the complex \([Co{(en)_2}C{l_2}]Cl\) will be: (en = ethylenediamine) ...
Number of possible isomers for the complex [Co(en)2Cl2]Cl will be: (en = ethylenediamine)
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 2
(D) 1
Solution
The given complex has stereoisomers and it does not have structural isomers. One of the isomers of this complex can rotate the plane of the polarized light. It also possesses geometrical isomer/s.
Complete step by step solution:
Isomers are the species which have the same molecular formula but different properties. Isomers can be divided into two main categories; structural isomers and stereoisomers. Structural isomerism can also be divided into categories like linkage isomerism, coordination isomerism, ionization isomerism and solvate isomerism.
- The isomers in the complex [Co(en)2Cl2]Cl can be shown by the cationic part [Co(en)2Cl2] only.
- This part cannot show structural isomerism. It will however show geometrical isomerism.
- We know that stereoisomers are of two types; geometric isomers and optical isomers.
- The given compound will have two geometric isomers; cis and trans. The structures of both are shown below.
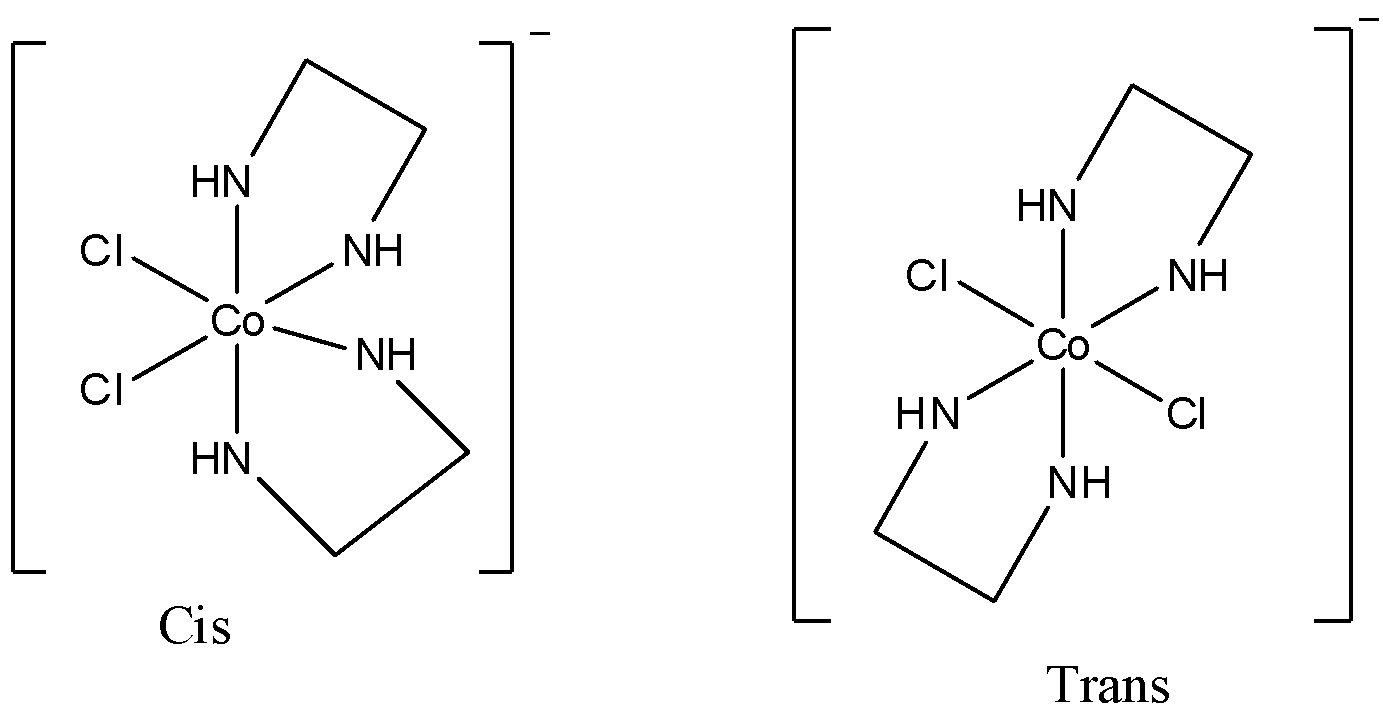
Now, we will see whether any optical isomer will be there or not.
- Optical isomers are the mirror images of the compounds that cannot be superimposed on each other. So, the cis isomer can form such two isomers (including itself) that are enentiomers. The optical isomers are named as dextro and laevo depending upon its characteristic to rotate the plane polarized light. So, the isomer of cis-[Co(en)2Cl2]Cl compound can be shown as
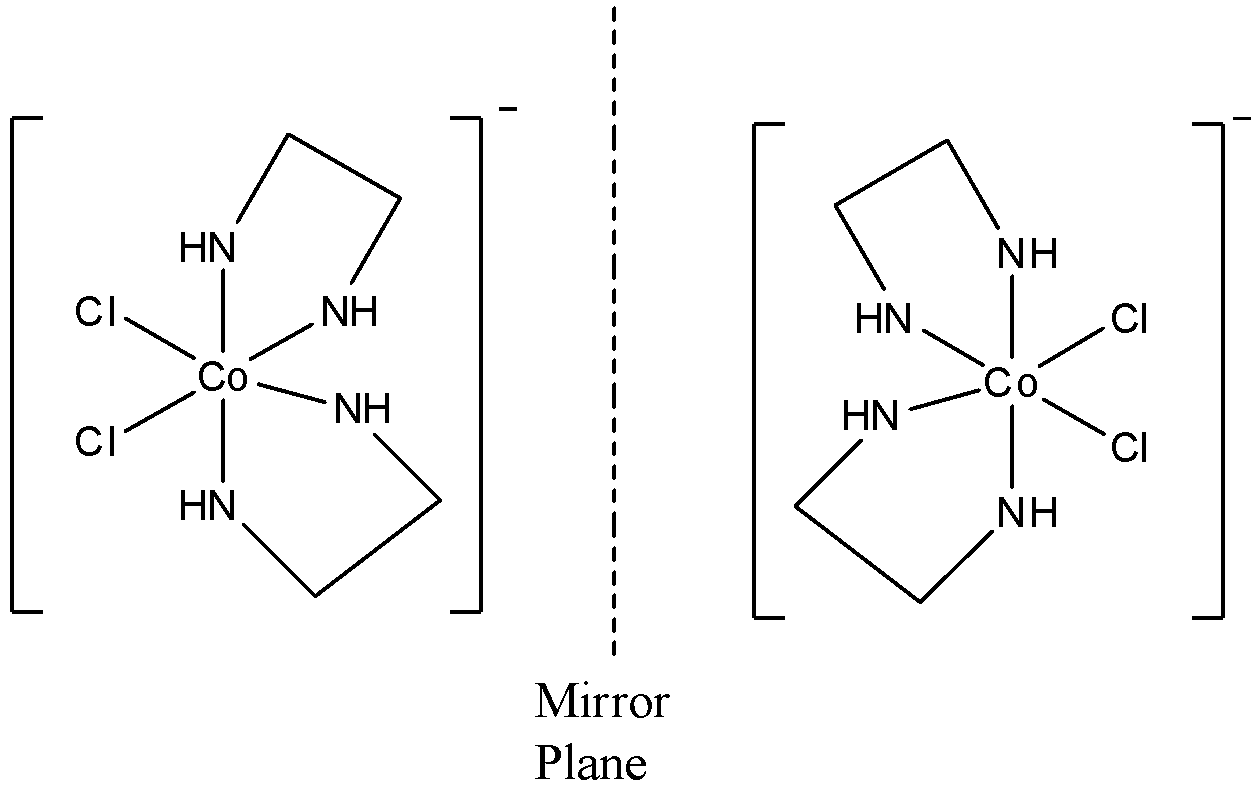
- Here, one isomer is laevorotatory and one is dextrorotatory.
- Thus, we found that there are a total 3 isomers of the given compound.
So, correct answer is (A)
Note: Note that most of the octahedral complexes involving didentate ligands can show optical isomers. Remember that we cannot predict which isomer will be dextrorotatory and which will be laevorotatory. We need to find it experimentally.
