Question
Question: Number of oxygen atoms in lipid molecules is always ......... as compared to the number of carbon at...
Number of oxygen atoms in lipid molecules is always ......... as compared to the number of carbon atoms
(A) Less
(B) More
(C) Equal
(D) Double
Solution
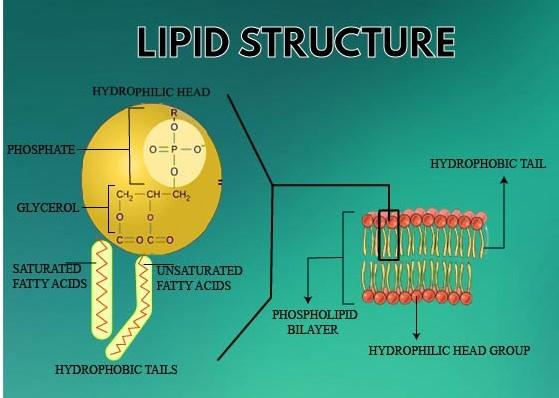
Lipid is a glycerol molecule that is bonded to long hydrocarbon chains and other molecules like phosphate group, etc. Lipid is the main component of animal cells and plant cells. In lipids that element is present in greater amounts that are non-metallic and are tetravalent.
Complete answer:
A hydrocarbon chain is a type of molecule that consists of hydrogen and carbon only. Oxygen is also present in lipid molecules but the major portion is carbon as carbon is also present in the hydrocarbon chain and lipid has a good amount of hydrocarbon chain present.
Additional Information: Lipid is defined as a substance that is not soluble in water but soluble in alcohol, ether, and chloroform which are also known as non-polar solvents
They are a crucial component of living cells. alongside carbohydrates and proteins. Lipid is also one of the main components of animal and plant cells. Lipids are the polymers of fatty acids that contain an extended, non-polar hydrocarbon chain with a little polar region containing oxygen. Lipids are majorly classified into two categories i.e Simple lipid and Complex lipid.
Simple lipids are esters of fatty acid with various alcohols, It includes fats and waxes.
Complex lipids are esters of fatty acid with various alcohol and besides, some different groups are also attached. For example, if phosphorus is added, it is known as phospholipids.
So, the correct answer is ‘Less'.
Note: As we are aware that the term ‘lipid’ is typically used as a synonym for fats, but fats are a subgroup of lipids called triglycerides. This means that all fats are lipids but all lipids are not fats.
Vitamins A, D, E, and K are called the fat-soluble vitamins, because they're soluble in organic solvents and are absorbed and transported in a manner just like that of fats.