Question
Question: Number of asymmetric carbon in \[\alpha - D( + ) - \] glucose is: A. 4 B. 6 C. 5 D. 3...
Number of asymmetric carbon in α−D(+)− glucose is:
A. 4
B. 6
C. 5
D. 3
Solution
An asymmetric carbon is a carbon atom which is attached to four different groups of atoms on its four valence sites. It is also known as chiral carbon and has the tendency to bend or rotate a plane polarized light in either clockwise direction or anticlockwise direction.
Complete step by step answer:
The α−D(+)− glucose which is also known as alpha-dextrose or alpha-D-GLC, belongs to a specific class of organic compounds that are known to be hexose. These are monosaccharides in which the sugar unit is a six-carbon containing moiety. α−D(+)−Glucose exists as a solid that is soluble in water and in a very weak acidic compound (based on its value of pKa ). Traces of α−D(+)−glucose have been found in human epidermis and intestine tissues. It has also been detected in multiple biofluids, such as faecal matter and saliva in the mouth. Within the cell, α−D(+)−glucose is primarily located in the cytoplasm, in the matrix part along with the other cell organelles. α−D(+)−glucose is found in all eukaryotes that ranges from yeast to humans. There are in total, five chiral carbons that are present in α−D(+)−glucose. The structure of the compound is as follows:
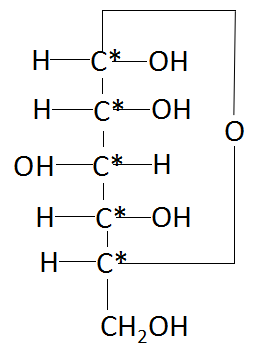
In the above structure, the carbon atoms marked by a star are the chiral carbon atoms which have four different groups attached to them.
Thus, the correct option is C i.e 5.
Note:
α−D(+)− glucose participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, α−D(+)−glucose can be converted into glucose 6-phosphate through the action of the enzyme hexokinase-2. Furthermore, Alpha-D-Glucose can be converted into β−D(+)−glucose through the action of the enzyme aldose 1-epimerase.
