Question
Question: No. of structural isomeric alkenes (molecular formula \( = \,{C_6}{H_{12}} \) ) which all give n-hex...
No. of structural isomeric alkenes (molecular formula =C6H12 ) which all give n-hexane on hydrogenation in presence of metal catalyst is:
(1)2
(2)3
(3)4
(4)5
Solution
Hint : Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. The general structural formula of alkenes is CnH2n . The given alkene, C6H12 , contains six carbon atoms and one double bond between two carbon atoms. On hydrogenation, the alkene gets reduced i.e., hydrogen atoms get added to the double bond to form a saturated alkane.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To find out the possible number of structural isomers of C6H12 that give n-hexane (straight chain of C6H14 ) on hydrogenation, we must try out hydrogenation reactions with each isomer. For hydrogenation reactions, we can use Palladium (Pd) as a metal catalyst.
Let us start with hex−1−ene :
CH3−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH=CH2H2/PdCH3−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH3
hex−1−ene n-hexane
Hydrogenation of hex−2−ene gives:
CH3−CH2−CH2−CH=CH−CH3H2/PdCH3−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH3
hex−2−ene n-hexane
Hydrogenation of hex−3−ene :
CH3−CH2−CH=CH−CH2−CH3H2/PdCH3−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH2−CH3
hex−3−ene n-hexane
These are the possible straight chain isomers of C6H12 .
Now let us check the hydrogenation of a simple branched chain isomer of C6H12 .
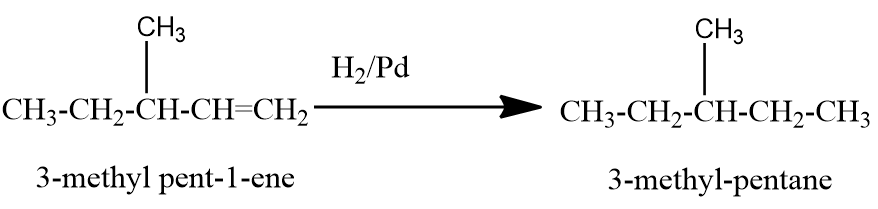
Here we can see that the end product is not n-hexane. Similarly, other branched chain isomers of C6H12 will give branched chain alkanes only as a product. Therefore, the structural isomeric alkenes of C6H12 that give n-hexane on hydrogenation in presence of metal catalysts are hex−1−ene , hex−2−ene and hex−3−ene .
The right option is (2)3 .
Note :
Hydrogenation reaction is an exothermic reaction between a hydrogen molecule - H2 and an organic compound in the presence of metal catalysts. Group 10 metals like NI, Pd and Pt are mainly used as catalysts in this reaction to reduce the compounds. It is a common method used to convert unsaturated organic compounds to saturated compounds.
