Question
Question: Nitrosyl ligand binds to d-metal atoms in linear and bent fashion and behaves , respectively as A....
Nitrosyl ligand binds to d-metal atoms in linear and bent fashion and behaves , respectively as
A.NO+ and NO+
B.NO+ and NO−
C.NO− and NO−
D.NO− and NO+
Solution
Nitrosyl complexes or metal nitrosyl complexes are complexes which contain nitric oxide, NO bonded to the transitional metal. Of the many kinds of the nitrosyl complexes, they differ both in co ligand and structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Most complexes which have NO ligand may be seen or viewed as a nitrosyl cation NO+ . It feeds two electrons to the metal and in return accepts electrons from the metal via back-bonding.
The M−N−O present in nitrosyl complexes are usually linear, or have no more than 15∘ from linear. But in some complexes, however, it is noticed, especially when back-bonding is a little less important, the M−N−O angle can strongly deviate from 180∘ .
We will see that, in NO+ structure, there exists a triple bond between N and O− atoms and two electrons which act as a lone pair of electrons or coordinate, so the angle between M−N−O is 180∘
While in NO− structure double bond exist between N and O− atoms while the 4{\text{ }}{e^\\_} acts as two lone pairs of electrons , so only one lone pair of electron coordinate with metal atom.
Suppose for a metal M the bonding with NO+ goes as -
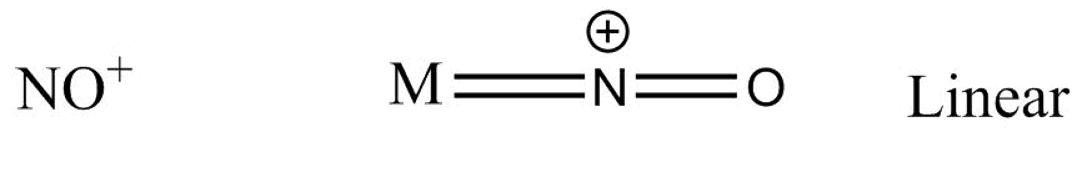
Which gives us a linear structure.
And bonding with NO− goes as –
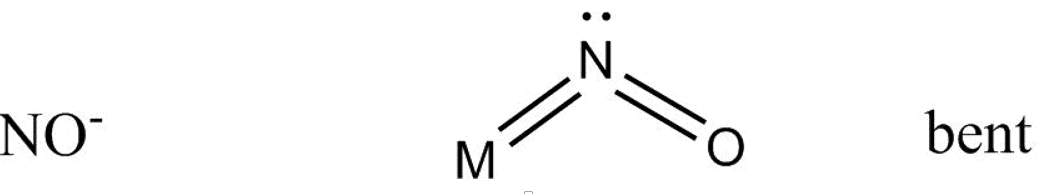
Which gives us a bent structure.
Therefore we can conclude that for the mentioned question,
Option (B). NO+ and NO− is the correct answer.
Additional information –
The linear and bent NO ligands can be distinguished using infrared spectroscopy. Linear M−N−O groups absorb in the range 1650−1900 cm−1, where as, the bent nitrosyls tend to absorb in the range of 1525−1690 cm−1. They differ in their vibrational frequencies and it reflects the differing N−O bond orders for linear (triple bond) and bent NO (double bond).
Note:
The bent NO ligand is sometimes described as the anion, NO−. Examples for such compounds are the organic nitroso compounds, such as nitrosobenzene. For example a complex with a bent NO ligand is trans−[Co(en)2(NO)Cl]+
