Question
Question: Nitrogen molecule is a nonpolar covalent molecule. (A) True (B) False...
Nitrogen molecule is a nonpolar covalent molecule.
(A) True
(B) False
Solution
We know that non- polar molecules are also known as hydrophobic molecules which means water fearing and will not dissolve in water. Also, we know that covalent bond is a bond formed by the sharing of atoms. So nonpolar covalent bonds are formed when a pair of electrons are shared between two or more atoms to form a molecule where the two atoms have the same electronegativity.
Complete answer: We already know that nitrogen is a non-metal which belongs to group 15 of the periodic table. The atomic number of nitrogen is 7 . The nitrogen molecule is a colorless, odorless and tasteless inert gas at room temperature.
As nitrogen has an atomic number of 7 so it will have 5 electrons in its valence shell. Therefore, it needs only three more electrons to complete its octet. So, for this there will be mutual sharing of three pairs of electrons between two atoms of nitrogen and will thus form a triple bond.
For the better explanation we will draw and depict how N2 will be formed.
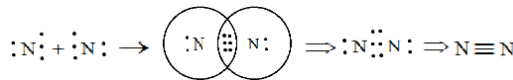
So here we see that nitrogen is forming a triple bond by sharing a total of three pairs of electrons and thus completing its octet and gaining stability. It has zero dipole moment as the two nitrogen atoms present in nitrogen molecules have the same electronegativity hence zero electronegativity difference.
So, it is true that the nitrogen molecule is a non-polar and a covalent molecule.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note: Nitrogen gas is an unreactive gas because the nitrogen atoms are bonded by a triple bond. So, this strong triple bond requires a high energy in order to break it. Hence the triple bond makes the nitrogen molecule a highly stable compound. Here ‘to complete its octet’ means that there should be eight electrons present in the valence shell of the atom. Helium is an exception to the octet rule as it only has two electrons in its valence shell.
