Question
Question: Nitration of phenyl benzoate yields the product: A)  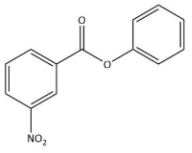
B) 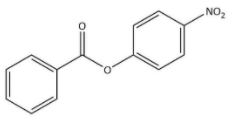
C) 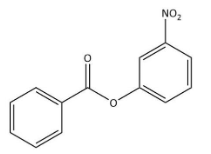
D) 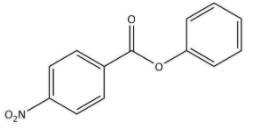
Solution
We know that the presence of electron withdrawing groups such as NO2, CN etc. at o-and p-positions but not at m-positions with respect to the halogen greatly activates the halogen towards nucleophilic displacement. We also know that the number of such groups at o- and p-positions with respect to the halogens varies directly with the reactivity of the haloarene.
Complete answer:
We know that the ring which is attached to the O- atom, in that the nitro group enters and as the result of it C6H5COO− group gets activated. It is known that it will not get into the ring to which the carbonyl group as it will deactivate the C6H5COO− group. We can now say that the C6H5COO− group is ortho and para directing in nature.
The chemical equation that represents the formation of 4-nitrophenyl benzoate is shown as follows.
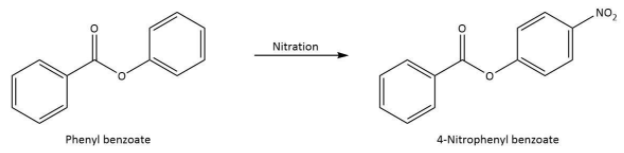
Thus, we can conclude the nitration of phenyl benzoate yields 4-nitrophenyl benzoate.
Hence, we can conclude that the correct option is B.
Note: We know that the presence of electron withdrawing groups at o- and p-position but not at m-positions with respect to the halogens activates the aryl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. The number of nitro groups at o- and p-positions increases, the stabilization of the resulting carbanion increases due to more resonating structures which results in the greater reactivity of the corresponding aryl halide.
