Question
Question: Nitration of phenol is an example of: (a)- Nucleophilic addition (b)- Nucleophilic substitution ...
Nitration of phenol is an example of:
(a)- Nucleophilic addition
(b)- Nucleophilic substitution
(c)- Electrophilic substitution
(d)- Electrophilic addition
Solution
When nitric acid reacts with phenol either nitrophenol or picric acid is formed based on the reactants taken. Nitro molecule (NO2) is an electrophile. The nitro group is attached to the phenol by removing the hydrogen atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Phenols undergo an Electrophilic substitution reaction. An example of an Electrophilic substitution reaction is the nitration of phenol.
There are 2 processes of nitration of phenol:
(i)- With dilute nitric acid: When dilute nitric acid at 293 K is used, phenols give mononitrophenols i.e., a mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol. Nitro molecule (NO2) is an electrophile. The nitro group is attached to the phenol by removing the hydrogen atom. However, 2-nitrophenol predominates over 4-nitrophenol probably due to the stabilization of the transition state leading to the formation of 2-nitrophenol due to the intramolecular H-bonding. The reaction is given below:
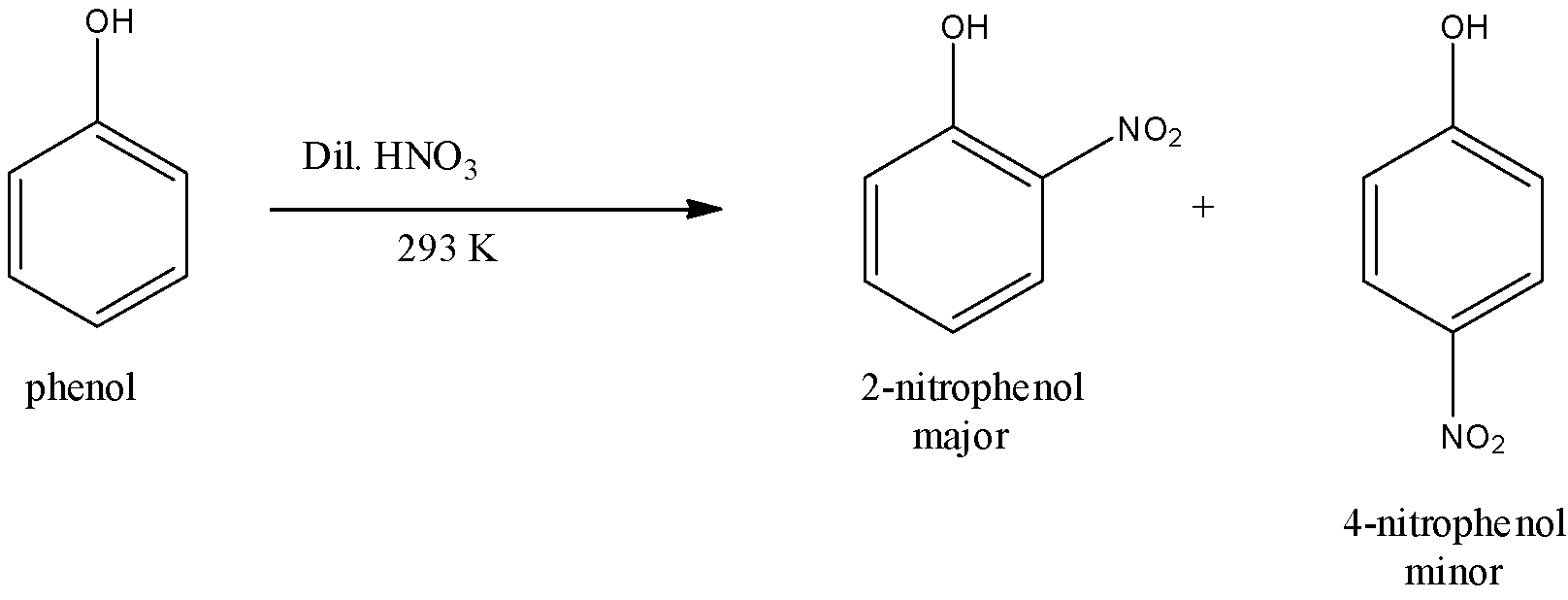
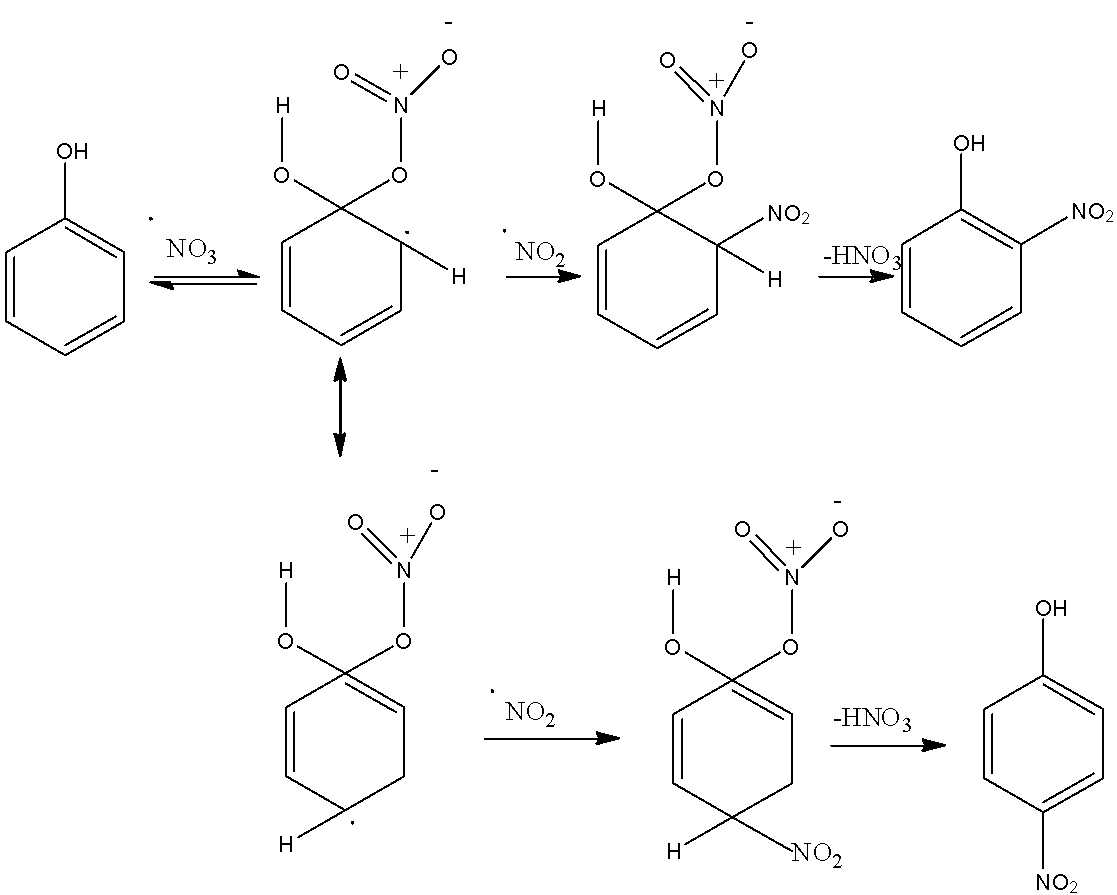
The mechanism of nitration is given below:
The intramolecular hydrogen bonding of 2-nitrophenol is given below:
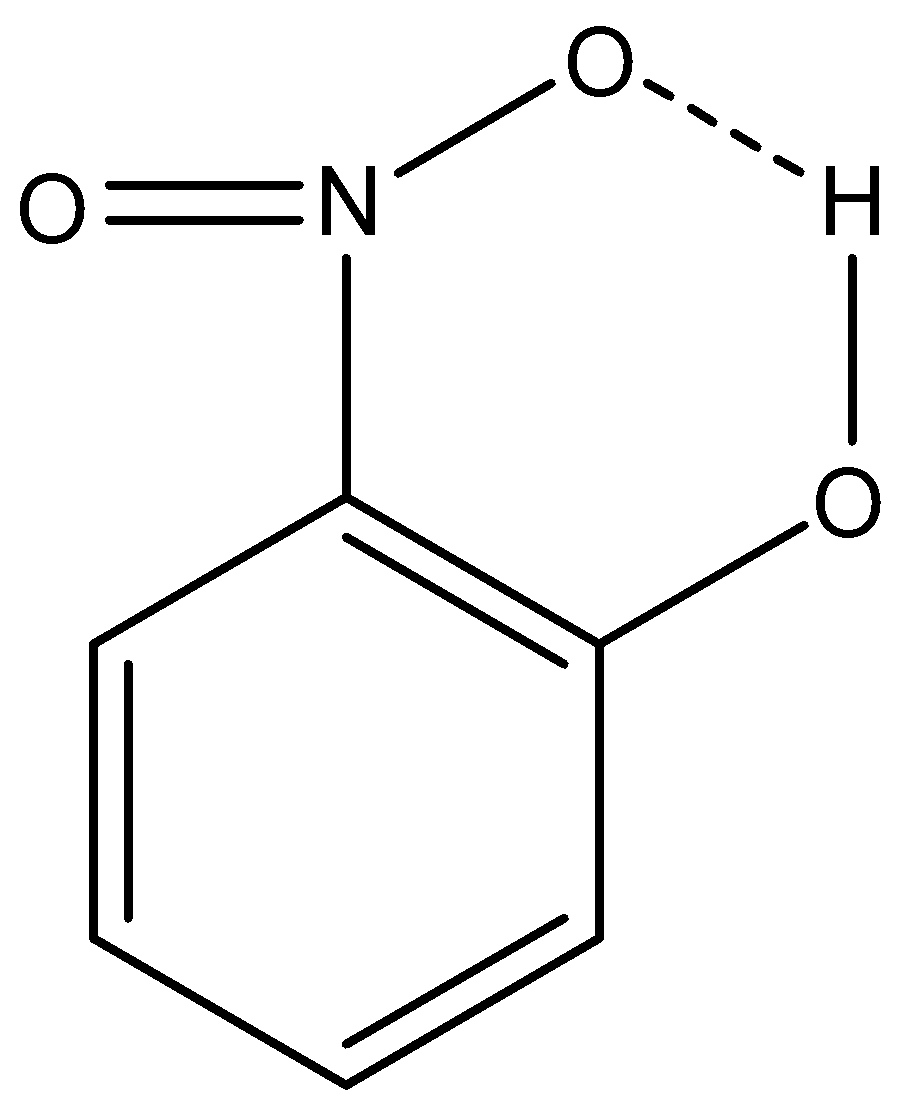
This intramolecular hydrogen bonding is not possible in 4-nitrophenol.
(ii)- With concentrated nitric acid: When the phenol is reacted with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid gives a trisubstituted phenol called 2,4,6-Trinitrphenol or it is commonly called picric acid. The yield is poor since most of the phenol is oxidized by concentrated nitric acid. The reaction is given below:
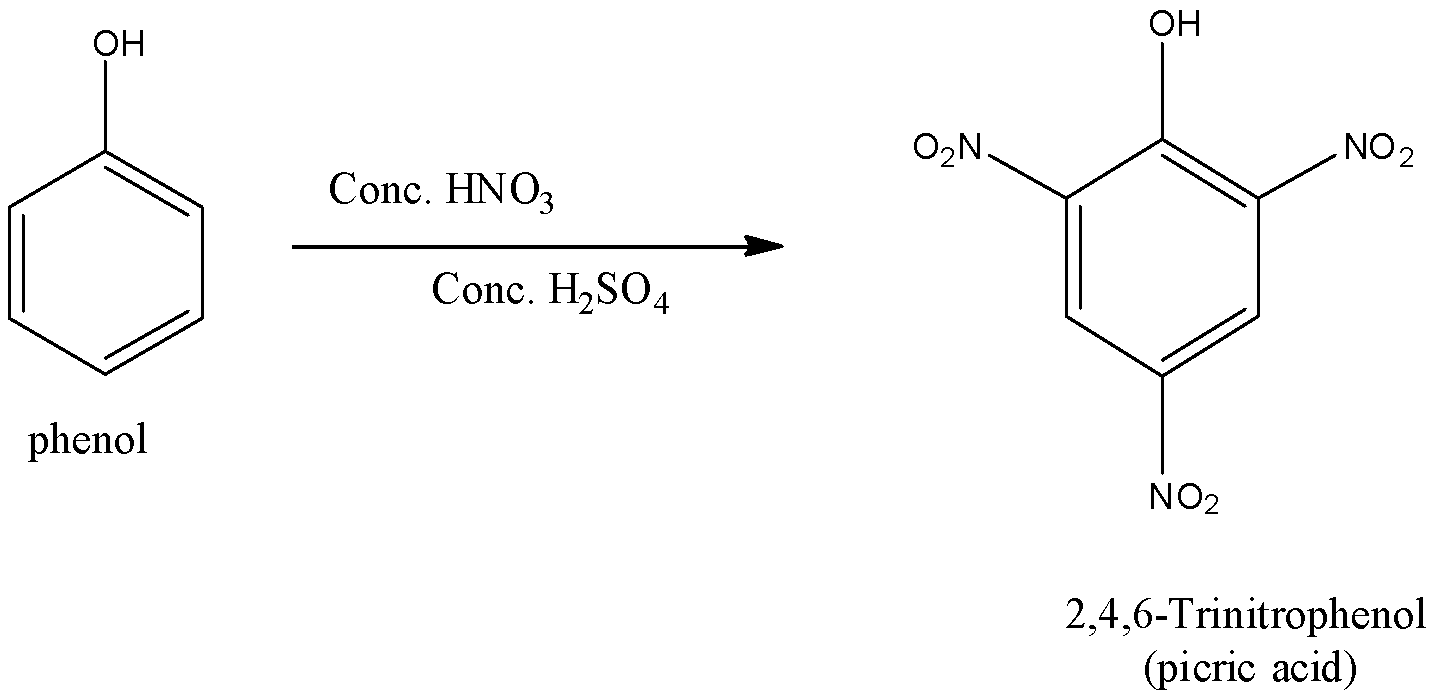
So, the correct answer is an option (c)- Electrophilic substitution.
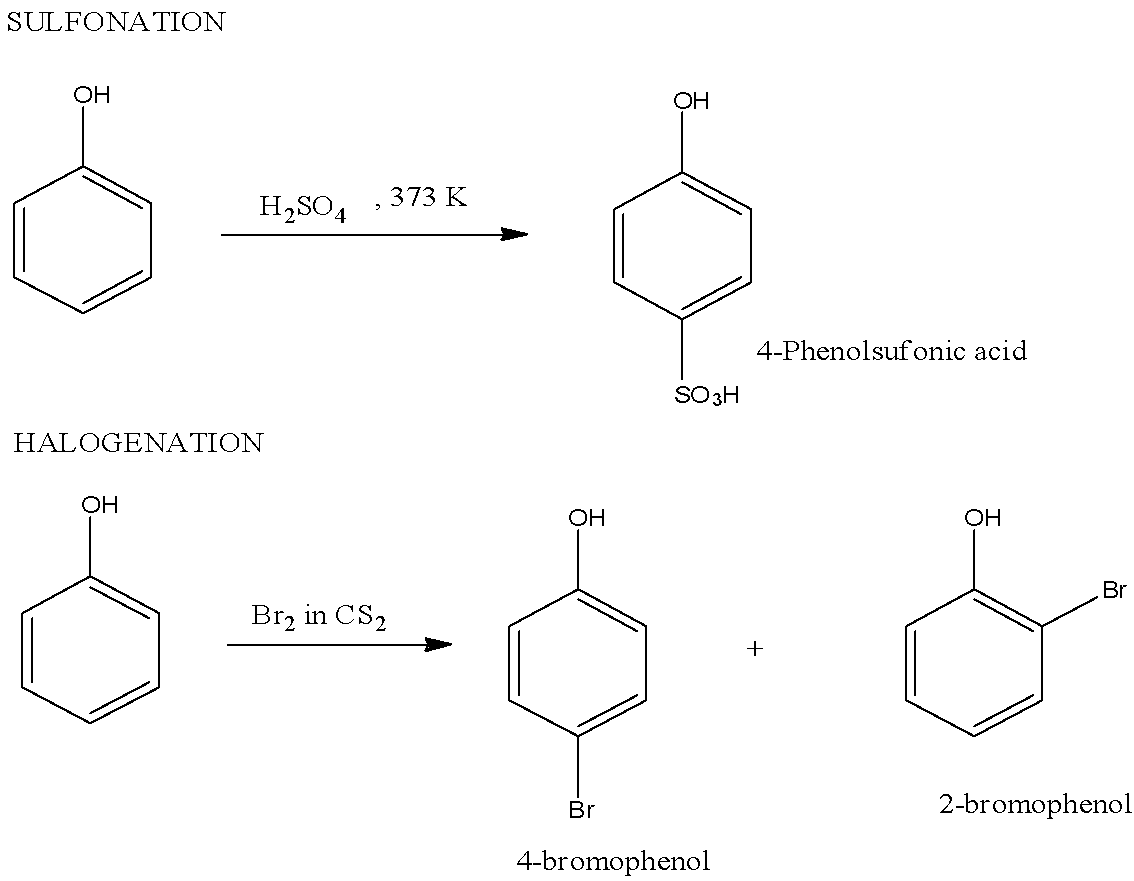
Note: Other examples of Electrophilic substitution reactions of phenol are halogenations in which halophenols are formed, sulfonation in which 4-Phenolsulfonic acid is formed, etc. The reaction of halogenations and sulfonation is given below: