Question
Question: Neopentyl chloride on reaction with ethanolic KOH is likely to: (a)Neopentyl alcohol (b)pentylen...
Neopentyl chloride on reaction with ethanolic KOH is likely to:
(a)Neopentyl alcohol
(b)pentylene
(c)2-methyl-2-butene
(d)undergo no reaction
Solution
Haloalkanes can undergo elimination reaction in the presence of concentrated solution of sodium or potassium hydroxide in ethanol. It is usually heated under reflux.
Complete step by step solution:
Elimination or dehydrohalogenation occurs in haloalkanes in the presence of ethanolic KOH or alcoholic KOH.
Alcoholic KOH, especially in ethanol, produce C2H5O−ions. These ions are much stronger than the base OH−ion. C2H5O−ion has the capability to abstract βhydrogen of the alkyl halide and can convert haloalkane to an alkene.
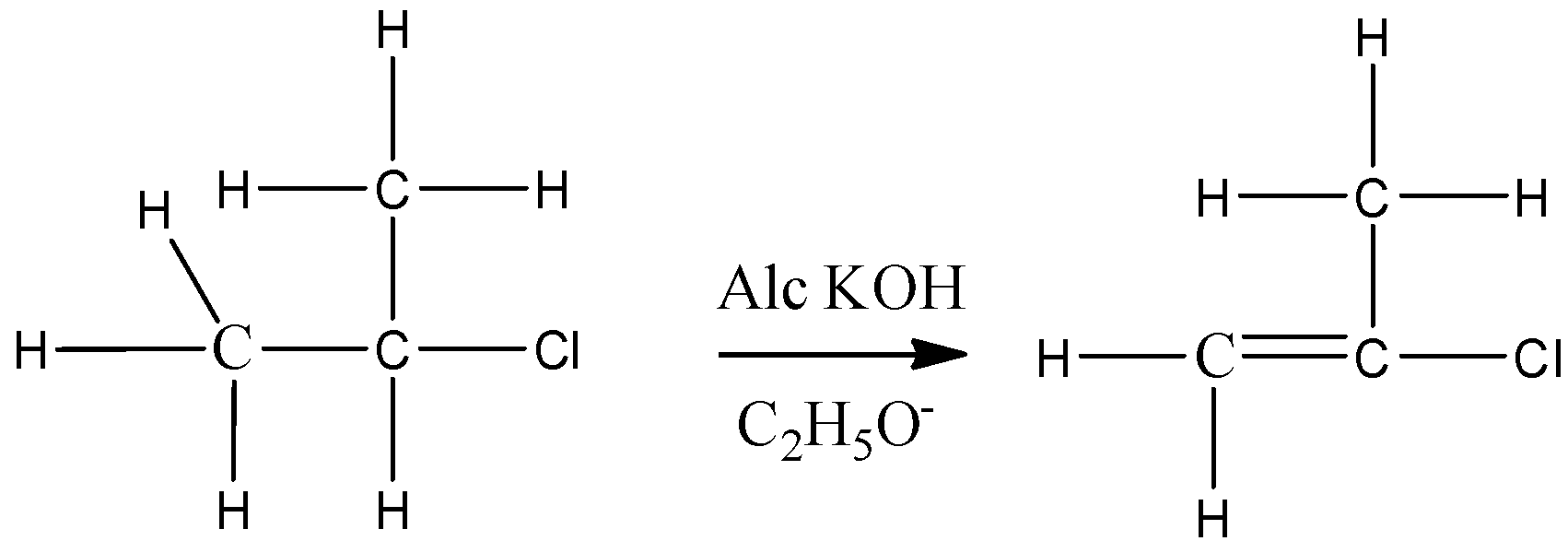
For elimination reactions to occur, there must be a βhydrogen in the alkyl halide, then only it can abstract this hydrogen and form a double bond. In case of neopentyl there is no βhydrogen.
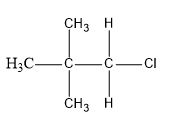
Therefore, it cannot undergo elimination reaction in the presence of ethanolic KOH.
The correct answer to the question is option (d).
Additional Information: This elimination reaction is also used for the preparation of alkenes. Alkenes of desired chain length can be prepared too and it follows Saytzeff's rule. The ease of dehydrohalogenation of different types of haloalkanes follows the order3o>2o>1o. This can be explained using saytzeff’s rule. The alkene with greater number of alkyl groups at doubly bonded carbon atoms is a preferred product. This implies that more substituted alkene is more stable and it is formed faster.
Note: We should always keep in mind that, while an elimination reaction occurs in a haloalkane, there must be aβhydrogen, otherwise the reaction will not happen.( Beta carbon atom is the carbon atom which is placed in second position from a functional group and the hydrogen directly bonded to beta carbon is called beta hydrogen). Because aldol condensation reaction is driven by the presence of beta hydrogen.
