Question
Question: Nasal aperture in Petromyzon is (a) Single (b) Paired (c) Many (d) Absent...
Nasal aperture in Petromyzon is
(a) Single
(b) Paired
(c) Many
(d) Absent
Solution
Petromyzon is an eel-like marine animal, with a distinct head, trunk, and tail. Nasal aperture is the bony inlet of the nose formed by the nasal and maxillary bones. It is present on the top of the head between the eyes.
Complete answer:
In Petromyzon, a simple nasal aperture is present on the top of the head between the eyes. Nasal aperture is single and median. Its head and trunk are cylindrical, the tail is laterally compressed. Lateral fins are altogether absent. Median fin system is poorly developed.
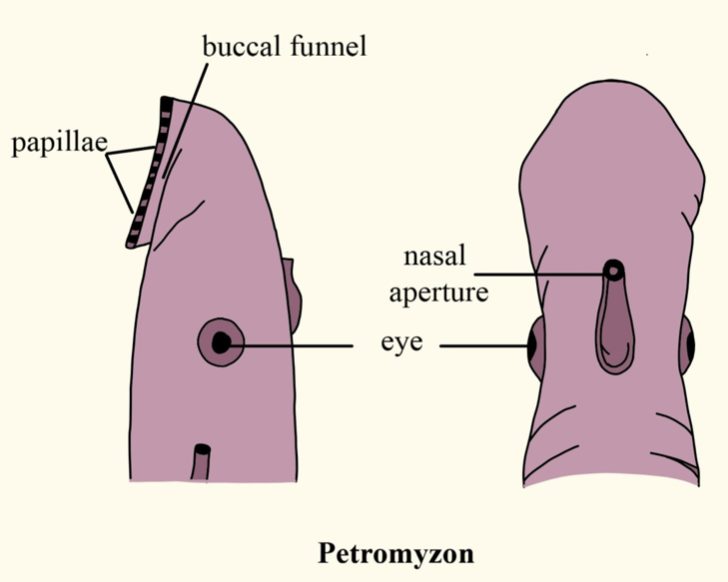
And it consists of two stumpy dorsal fins and a caudal fin. At the anterior end of the head, and directed downward, is a basin-like depression, called buccal funnel or oral sucker. It is surrounded by a marginal membrane, whose outer surface is provided with numerous sensory cirri and overlapping oral fimbriae. The inner side of the funnel is beset with radiating rows of horny teeth, born on cartilaginous plates.
Additional Information:
- Projecting from the bottom of the buccal funnel is a protrusible prominence often called the rasping tongue. It is armed with large horny teeth. Just above the tongue is the narrow mouth.
- Head bears a pair of well-developed, large and lidless lateral eyes, covered by transparent skin.
- On the mid-dorsal surface of the head is a median nostril. A little behind the eyes are the seven pairs of gill slits.
So, the correct answer is '(a) Single'.
Note:
- The skin of Petromyzon is smooth and heavily pigmented, without exoskeletal structures. The branchial or visceral skeleton of Petromyzon consists of a branchial basket, formed of nine pairs of branchial baskets.
- The digestive tract of Petromyzon is a straight and uncoiled tube, differentiated into the mouth, buccal cavity, pharynx, Oesophagus, intestine, rectum, and anus.
- The respiratory system of Petromyzon consists of seven pairs of branchial pouches or gill pouches, in the pharyngeal region.
