Question
Question: Name the photosynthetic organ and photosynthetic organelle in plants?...
Name the photosynthetic organ and photosynthetic organelle in plants?
Solution
Photosynthesis is a process that plants and other organisms utilise to transform light energy into chemical energy that can then be released to power the organism's activities through cellular respiration.
Complete answer:
The leaves contain the majority of mesophyll (photosynthetic plant tissue), making them the primary photosynthetic organ in plants - it looks like this:
Chloroplasts are organelles found inside the mesophyll. These organelles turn the sun's light energy into chemical energy that the plant can use. This is what a chloroplast looks like:
You'll observe small stacks of coin-shaped objects (thylakoids), which are where the action takes place. There are a slew of proteins inside the thylakoid's thin membrane that are dedicated to converting light into energy that the plant may use to thrive. Here's a more in-depth look at the procedure:
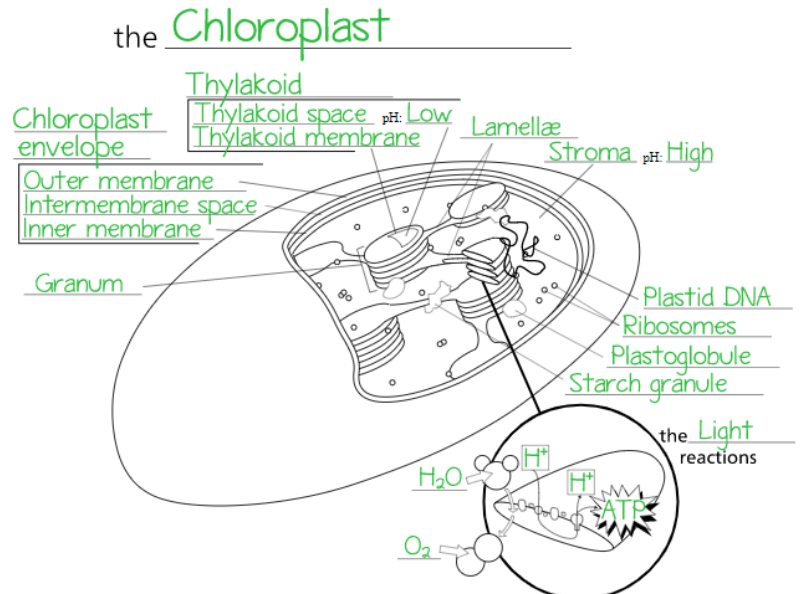
Chloroplasts are organelles in plant and algal cells that perform photosynthesis, in which the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll takes energy from sunlight, transforms it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while releasing oxygen from water.
Chloroplasts are a form of plastid, which is a circular, oval, or disk-shaped entity involved in food synthesis and storage. The presence of two pigments, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b, distinguishes chloroplasts from other types of plastids by their green colour. One of the functions of such pigments is to absorb light energy for the photosynthesis process. Other pigments found in chloroplasts, such as carotenoids, act as accessory pigments, capturing solar energy and passing it on to chlorophyll. Chloroplasts can be found in all green tissues of plants, although they are concentrated in the parenchyma cells of the leaf mesophyll.
Note:
Photosynthesis, the process by which light energy is transformed to chemical energy, resulting in the generation of oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds, takes place in the chloroplast, a structure found within the cells of plants and green algae. Endosymbiotic theory claims that chloroplasts and mitochondria (energy-producing organelles in eukaryotic cells) are descended from photosynthetic cyanobacteria, which are free-living close relatives of chloroplasts.
