Question
Question: Name the chemical reagents required in the following reactions: i. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\...
Name the chemical reagents required in the following reactions:
i. CH2=CH−CH2OH→CH2=CH−CHO
ii. CH3−COOH→CH3CONH2
Solution
In the first reaction, an alcohol is converted to an aldehyde. In the second reaction, carboxylic acid is converted to an amide.
Complete step by step solution:
i. Consider the reaction,
CH2=CH−CH2OH→CH2=CH−CHO
In the reaction, prop-2-ene-1-ol is converted to prop-2-enal.
In the reaction, alcohol prop-2-ene-1-ol is oxidized to the aldehyde prop-2-enal using oxidising agents. The oxidising agents that can be used to convert alcohols to aldehydes are as follows:
1. Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) solution.
2. Collins reagent (chromium trioxide-pyridine complex).
3. Potassium dichromate in the presence of sulphuric acid.
4. Cu at 573 K.
In the reaction, during oxidation of alcohol, one oxygen atom of the oxidising agent eliminates one hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl (−OH) group of the alcohol and one hydrogen atom attached to the carbon atom. Thus, a water (H2O) molecule is eliminated in the reaction.
The reaction mechanism is as follows:
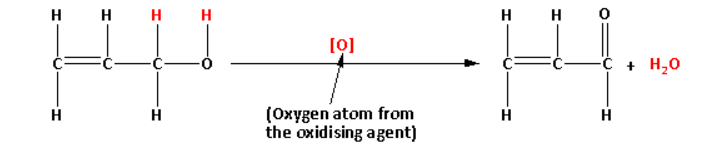
Thus, the chemical reagents required in the reaction are:
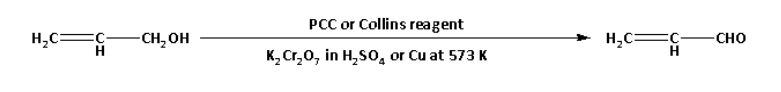
ii. Consider the reaction,
CH3−COOH→CH3CONH2
In the reaction, acetic acid is converted to acetamide.
In the reaction, carboxylic acid i.e. acetic acid is converted to the amide i.e. acetamide. But the acetic acid does not directly convert to acetamide. The reaction occurs by formation of an intermediate which is ammonium salt of an acid. The reagents that can be used to convert carboxylic acid to amides are as follows:
1. Ammonia (NH3).
2. Ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) in liquid ammonia.
3. N,N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC).
In the reaction, the carboxylic acid is heated with any of the given reagents. This leads to the formation of ammonium salt of carboxylic acid which decomposes on heating and gives amide.
The reaction mechanism is as follows:
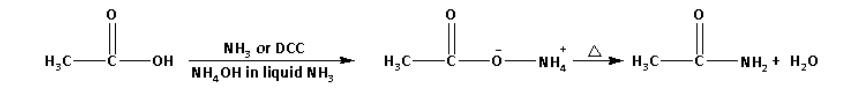
Thus, the chemical reagents required in the reaction are:
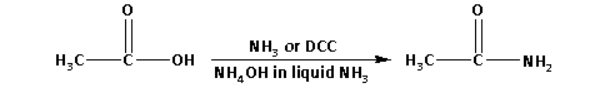
Note:
To convert alcohols to aldehydes oxidising agents are used. To convert carboxylic acids to amides ammonia or its compounds are used.
