Question
Question: \({NAD+}\) and \({NADP+}\) resemble each other in the ability to a) Give out a proton b) Take ...
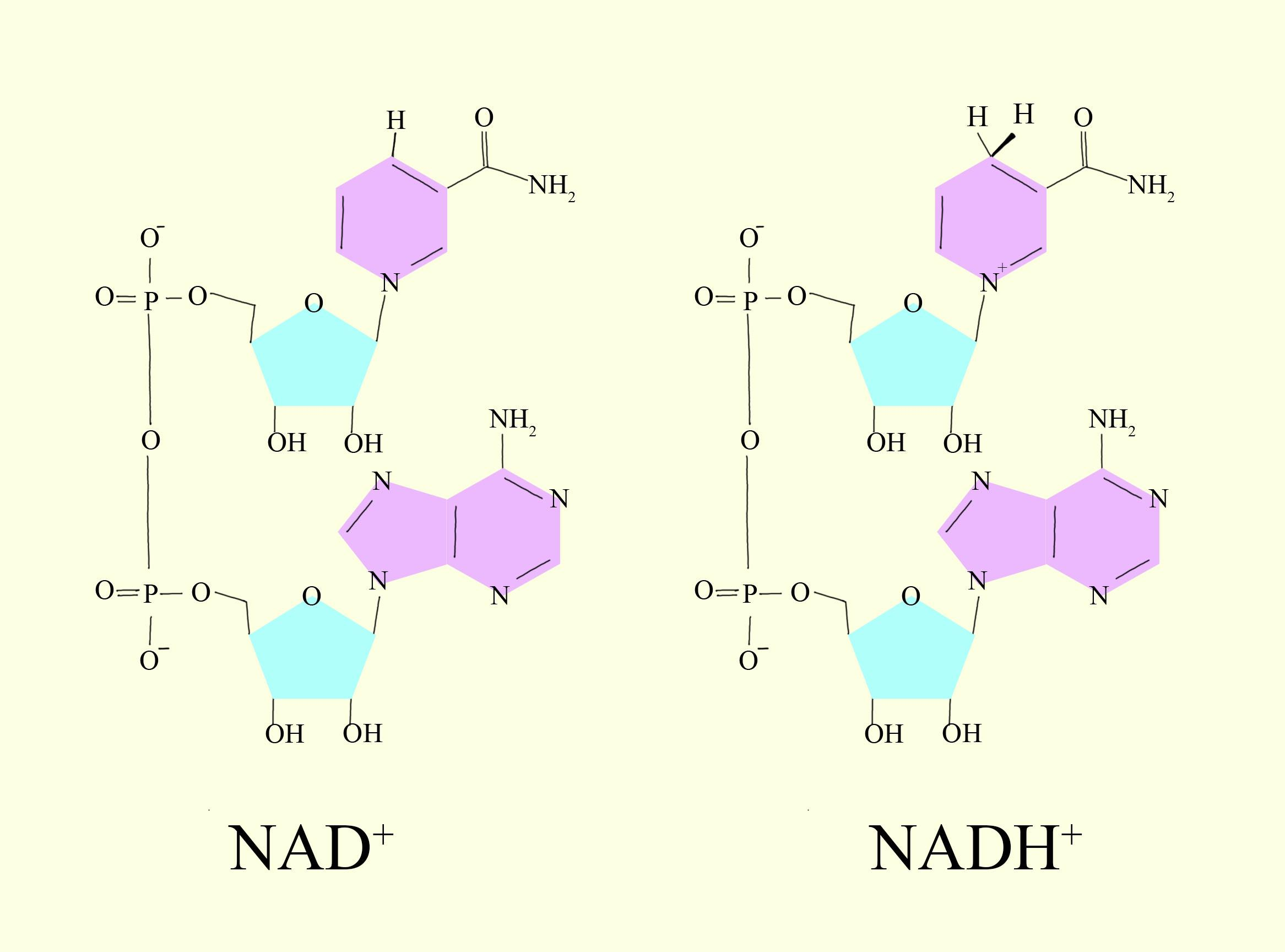
NAD+ and NADP+ resemble each other in the ability to
a) Give out a proton
b) Take up two electrons at one time
c) Take up two hydrogen atoms
d) Take up one electron at one time
Solution
The functions of NADH NAD+ and NADH and NADPH (NADP+ and NADPHare undoubtedly significant and distinct. So the regulation of the intracellular balance of NADH and NADPHis important The key enzymes involved in the regulation are NAD kinase and NADP phosphatase.
Complete answer:
NADH is primarily involved in catabolic reactions, while NADPH participates in anabolic reactions and in defense against oxidative stress. NAD+ functions as a substrate for mono- and poly-ADP ribosylation and is involved in the formation of cyclic ADP ribose and in histone deacetylation which is required for transcriptional silencing. Poly ADP ribosylation has been implicated in the regulation of several processes, including DNA repair, transcription, and apoptosis.
On the other hand, NADP+ is a substrate used in the synthesis of nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate. This is a potent intracellular Ca2+ mobilizing messenger that triggers Ca2+ release from lysosomal Ca2+ stores, which are independent of the stores activated by cyclic ADP ribose and inositol-1,4,5- triphosphate. Considering these significant and distinguishable functions of NADH and NADPH, regulation of the intracellular balance of NADH and NADPH is thought to be important in cells.
Additional Information: NAD participates in many redox reactions in cells, including those in glycolysis and most of those in the citric acid cycle of cellular respiration.
NADP is the reducing agent produced by the light reactions of photosynthesis and is consumed in the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis and used in many other anabolic reactions in both plants and animals.
Under the conditions existing in a normal cell, the hydrogen atoms shown in red are dissociated from these acidic substances.
So the correct answer is ‘Take up two electrons at one time ‘.
Note: There have been numerous metabolic engineering studies in which the metabolic network of an organism has been altered by the addition of NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductase(s), or pathways including them. One of the most frequent goals of this type of approach is the efficient production of a given chemical of interest without the need for chemical synthesis or purifying enzymes, and ideally from renewable feedstocks and with a lower energy consumption due to the mild conditions at which reactions can be catalyzed by NADPH dependent oxidoreductases.
