Question
Question: n-factor of \({{H}_{3}}B{{O}_{3}}\) in aqueous solution will be: A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4...
n-factor of H3BO3 in aqueous solution will be:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Solution
H3BO3 is also called boric acid. Acids have a property of liberating H+ ions very easily when dissolved in a polar solvent. For acids, the n-factor is nothing but the number of replaceable H+ ions by the reaction of one mole of an acid.
Complete step by step answer:
- Before going to know about the n-factor for boric acid we should know the structure of it.
- The structure of the boric acid is as follows.
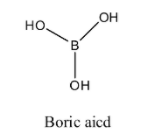
- Boric acid contains three hydrogens which are attached to three oxygen atoms.
- Even though boric acid contains three H+ ions the n-factor is not 3.
- Because the three hydrogens attached to boron through oxygen are not replaceable.
- Boron atom in boric acid acts as a Lewis acid (means electron deficient), then the lone pair of electrons present in the oxygen of water attack on boron in boric acid.
- The chemical reaction of boric acid with water is as follows.
H3BO3+2H2O→[B(OH)4]−+H3O+
- From the above reaction we can say easily that the n-factor for boric acid is 1.
- So, the correct option is A.
Note: n-factor for an acid or a base is not equal to the number of H+ ions or OH− ions present. n-factor for acids is nothing but the number of H+ ions are going to replaceable when an acid is going to reacts with water and for base n-factor will be the number of OH− ions are going to replaceable when a base is going to reacts with water.
