Question
Question: Mutarotation involves: (A) Racemisation (B) Diastereomer Isation (C) Optical resolution (D) ...
Mutarotation involves:
(A) Racemisation
(B) Diastereomer Isation
(C) Optical resolution
(D) Conformational inversion
Solution
Mutarotation is the change in optical relation observed when pure α−or β−anomers are dissolved in water.
It is possible when α−or β−anomers can interconvert.
Step by step answer: Let us discuss the terms given in question one by one:
Race misation: This is a process in which optically active compounds convert into an equal mixture of enantiomers with zero optical activity.
The mixture is also called racemic mixture. The mixture contains dextro- and laevo- rotatory isomers in equal quantity.
Siaslereomerisation: Let us explain thus with the following example.
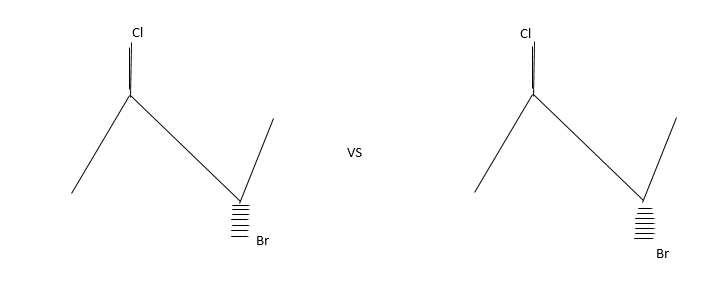
The compound contains both Bromine and chlorine atoms but they differed in the way they occupied three dimension dace.
These isomers are present in equilibrium and interconvertible.
Optical resolution: Optical resolution is a physical resolution at which an imaging device can capture an image.
Conformational inversion: Saturated cyclic six membered heterocycles i.e., cyclohexane can adopt one or more conformations that are free of torsion or bond angle strain.
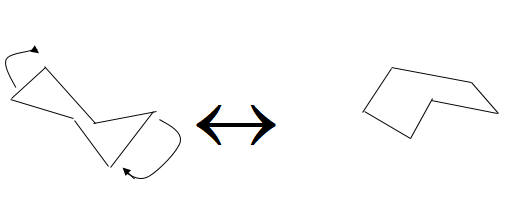
Mutarotation involves Diastereomer Isation.
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (B) Diastereomer Isation.
Note: Mutarotation is the change in optical rotation because of change in equilibrium between two anomers. The optical rotation of solution depends on the optical rotation of each anomer and their ratio in the solution. The αand βanomers are diastereomers of each other and usually have different specific rotations.
