Question
Question: Molecular axis is Z axis, then which of the following combinations of orbitals will result in format...
Molecular axis is Z axis, then which of the following combinations of orbitals will result in formation of σ molecular orbitals?
(A) px−px
(B) s−s
(C) pz−pz
(D) py−py
Solution
According to Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), atomic orbitals overlap to form new orbital called molecular orbitals in a molecule. These molecular orbitals are not identical to atomic orbitals and based on this theory there is no identity for atomic orbitals which are combined to form molecular orbitals.
Complete step by step solution:
Characteristics of Molecular Orbital Theory: The linear combination of atomic orbitals which leads to the formation of molecular orbitals. Like an atomic orbital, the molecular orbital is a probability density around a group of nuclei. The number of atomic orbitals will form an equal number of molecular atomic orbitals. If two molecular orbitals from two atomic orbitals combination, one molecular orbital is bonding and another one is antibonding. Bonding molecular orbital has lower energy than antibonding molecular orbital. Formation of sigma molecular orbital and anti-sigma molecular orbital will form when two s orbital overlap while assuming the Z-axis will be the molecular axis. Diagrammatic representation of the formation of sigma molecular orbitals by s-atomic orbitals “s+s”.
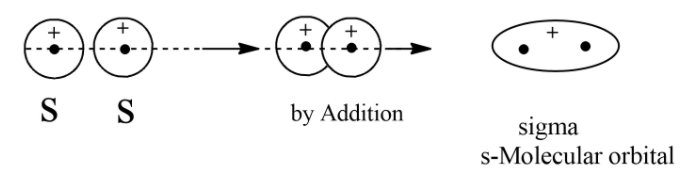
Hence, the s+s combination of orbitals will result in the formation of σ molecular orbitals.
Note: The molecular orbital which is formed by the additive overlap of constructive interference of waves has got less energy bonding molecular orbital (BMO). The molecular orbital which is formed by the subtractive overlap of destructive interference of waves has got more energy known as Anti-bonding Molecular Orbital (ABMO).
