Question
Question: Molarity of a given orthophosphoric acid solution is 3M. Its normality is: A. 9 N B. 0.3N C. 3...
Molarity of a given orthophosphoric acid solution is 3M. Its normality is:
A. 9 N
B. 0.3N
C. 3 N
D. 1 N
Solution
We need to understand equivalent concept [n factor*mole=equivalent]. Equivalent weight [E] of any element or substance is defined as the weight of element that combines or replaces 1g of ‘H’, 8g of ‘O’ or 35.5 g of Cl.
Complete step by step solution:
E=molar weight/n factor.
Since n-factor can change in any reaction equivalent weight is a variable quantity however molar weight is a fixed quantity. n-factor of base is acidity and it is defined as the number of moles of OH− ions given by one mole of base.
Normality = (no. of gram equivalents of solute)/volume of solution in L
Molarity= (no. of moles of solute)/volume of solution in L
Number of gram equivalents of solute=weight of solute/Equivalent weight
Equivalent weight=molecular weight/’n’
Normality=’n’*Molarity
n-factor is the valency factor or conversion factor. Orthophosphoric acid is a tribasic acid; it has three replaceable hydrogen ions per mole. For acids n-factor is basicity it is defined by the number of hydrogen ions replaced. n-factor for orthophosphoric acid is 3.
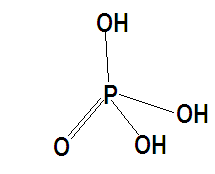
Substituting the values we are given with molarity =3M and n-factor =3.Therefore
Normality =3M*3=9N
Hence the correct option is option A.
Note: Number of moles of a substance=Weight of substance/Molecular weight
