Question
Question: Minimum \(F-S-F\) bond angle is present in: (a)- \(SS{{F}_{2}}\) (b)- \(S{{F}_{6}}\) (c)- \(...
Minimum F−S−F bond angle is present in:
(a)- SSF2
(b)- SF6
(c)- SF2
(d)- F3SSF
Solution
Bond angle can be measured as the angle between three atoms, keeping one atom as a central atom and it is forming a bond with the other two atoms. The molecule that has many atoms will have a small bond angle because of steric hindrance.
Complete answer:
The bond angle can be measured as the angle between three atoms, keeping one atom as the central atom and it is forming a bond with the other two atoms. So let us examine all the compounds in the options one by one.
(a)- SSF2, this compound is also written as S2F2 and is known as disulfur difluoride. It has two isomers, so the structure of the isomer that has an F−S−Fbond is given below:
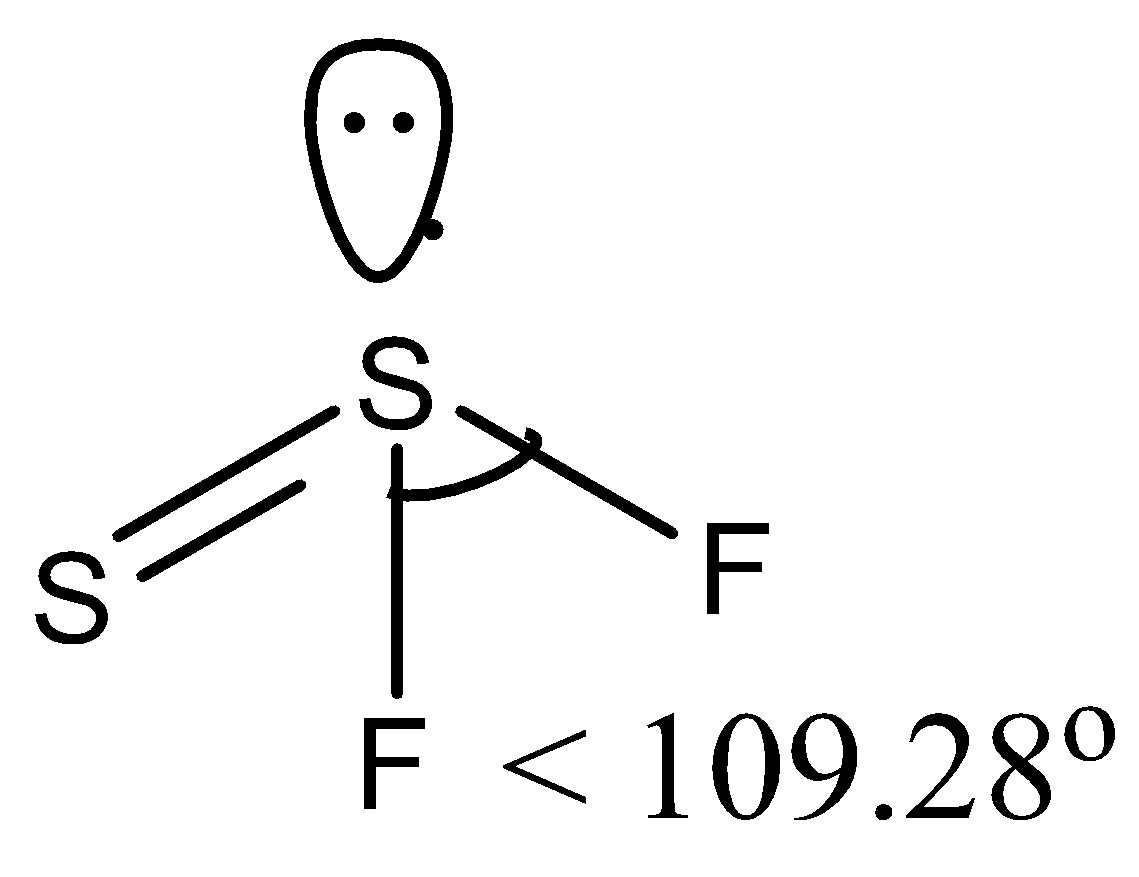
So there is a lone pair on the sulfur atom so the bond angle is reduced from the tetrahedral angle. So it has < 109∘28 !!′!! bond angle.
(b)- SF6, this compound is sulfur hexafluoride. This compound has regular octahedral geometry. So its structure is given below:
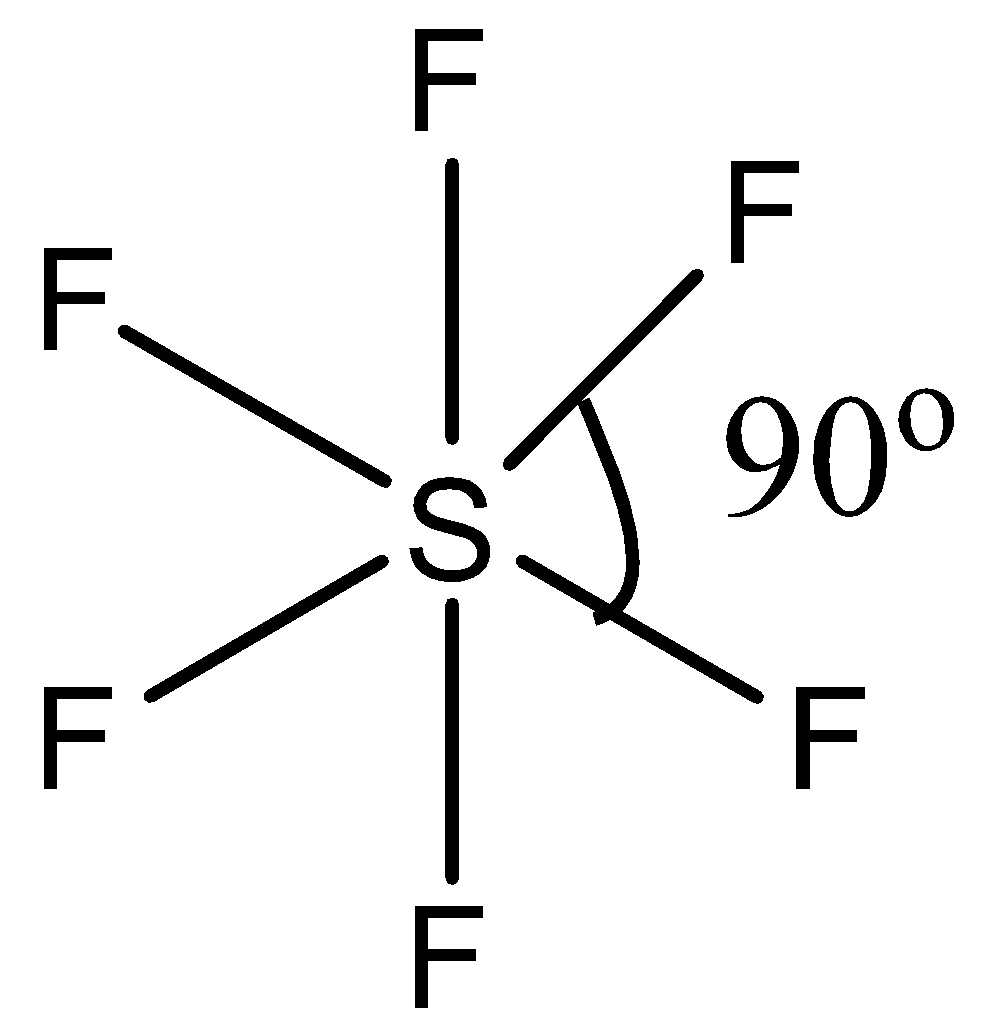
Since it has a symmetric structure, the bond angle is 90∘.
(c)- SF2, this compound is sulfur difluoride. In this compound, the sulfur has two lone pairs. So the structure is given below:
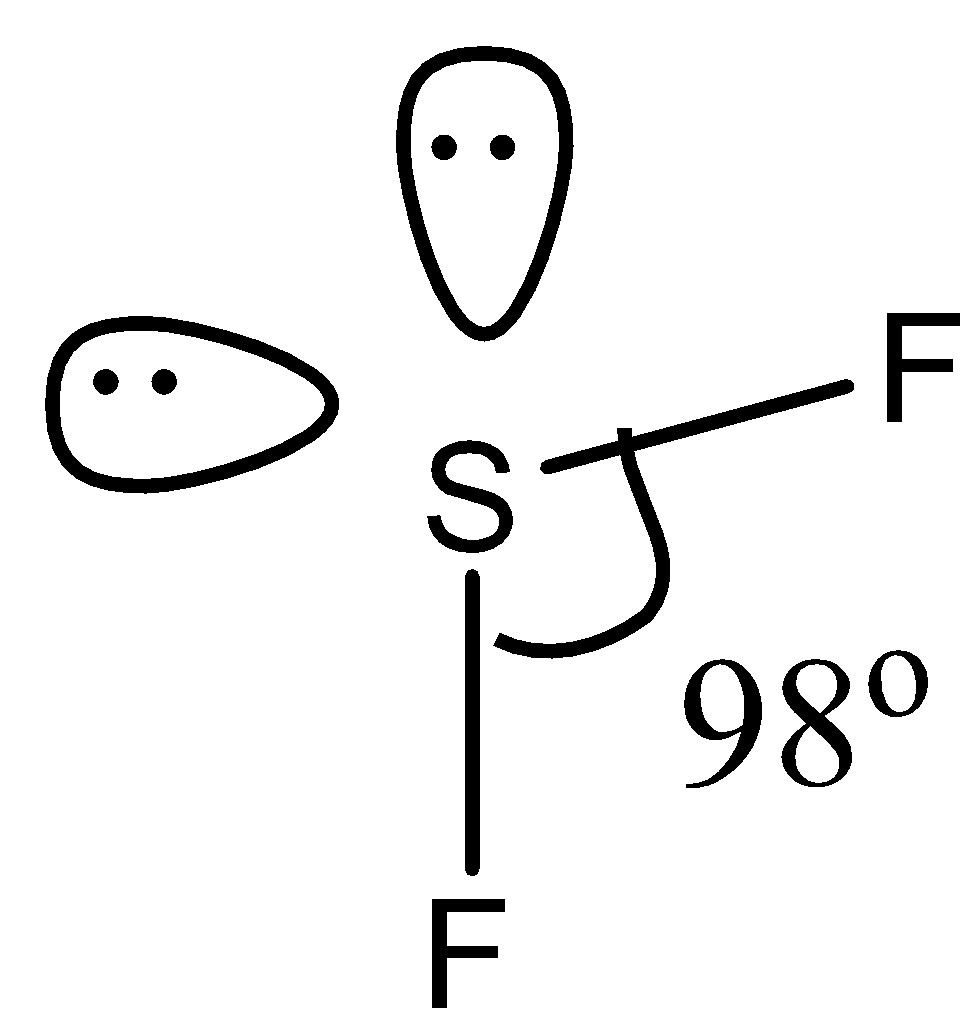
Due to the presence of two lone pairs, the bond angle is 98∘.
(d)- F3SSF, this compound is difluoro disulfur difluoride. Both the sulfur atoms have lone pairs. The structure is given below:
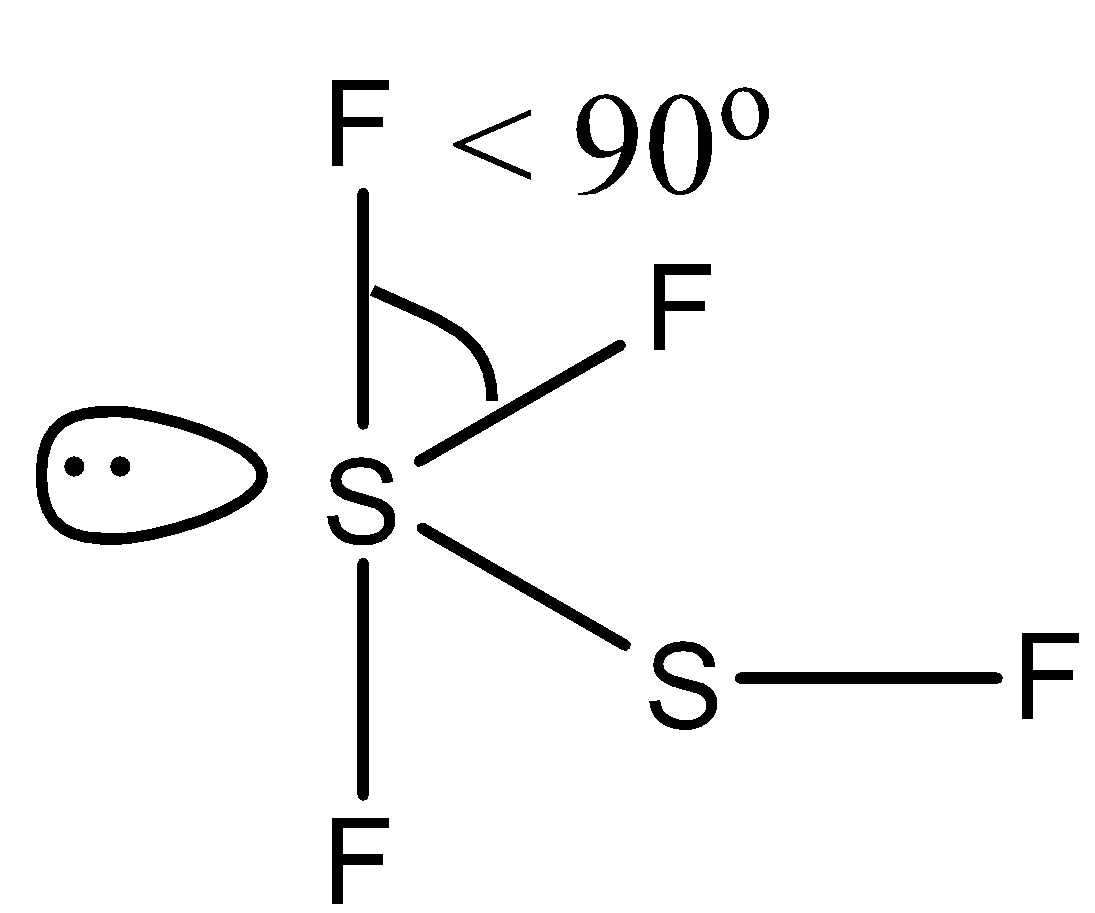
Due to the presence of lone pair the bond is reduced from right angle, i.e., < 90∘.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (d)- F3SSF.
Note:
It must be always noted that if the atom has a lone pair, then there will be repulsion between the bond and lone pairs and the bond angle of the compound will be affected. Lone pair-lone pair repulsion is greater than bond pair-bond pair repulsion.
