Question
Question: Methyl D- glucoside on reaction with \(HI{O_4}\)consumes two moles of reagent and produces the diald...
Methyl D- glucoside on reaction with HIO4consumes two moles of reagent and produces the dialdehyde A and mole of HCOOH. The result of this reaction proves that glucose has pyranose structure.
Solution
Saccharides: The unit structure of carbohydrates, are known as saccharides.
Pyranose structure: The saccharides which have six membered rings containing five carbon and one oxygen atom, are known as pyranose structure.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all we will discuss carbohydrates, saccharides, structures.
Carbohydrates: The sugar, starch and fibres found in fruits and vegetables, are known as carbohydrates. A carbohydrate is a molecule consisting of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with hydrogen and oxygen ratio as 2:1. So its empirical formula is as Cm(H2O)n.
Saccharides: The unit structure by which carbohydrates are formed, known as saccharides. Saccharides are divided into four groups as: monosaccharide, disaccharide, oligosaccharide and polysaccharide.
Monosaccharide: These are the simplest carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrates. For example: glucose, fructose.
Disaccharide: Two monosaccharides are joined together to form disaccharides. They are linked together by a covalent bond, known as glycosidic linkage. For example: sucrose, lactose.
Oligosaccharide:Carbohydrates containing three-ten molecules of saccharide, is known as oligosaccharide. For example: Raffinose
Polysaccharide: Carbohydrates containing more than ten molecules of saccharides, are known as polysaccharide. For example: starch.
Pyranose structure: The saccharides which have six membered rings containing five carbon and one oxygen atom, are known as pyranose structure.
Furanose structure: The saccharides which have five membered rings containing four carbon and one oxygen atom, are known as pyranose structure.
The molecular formula of glucose is C6H12O6. The structure of glucose is pyranose which has six membered rings containing five carbon and one oxygen.
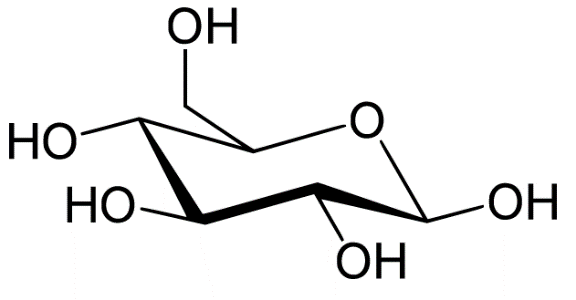
The reaction is as follows:
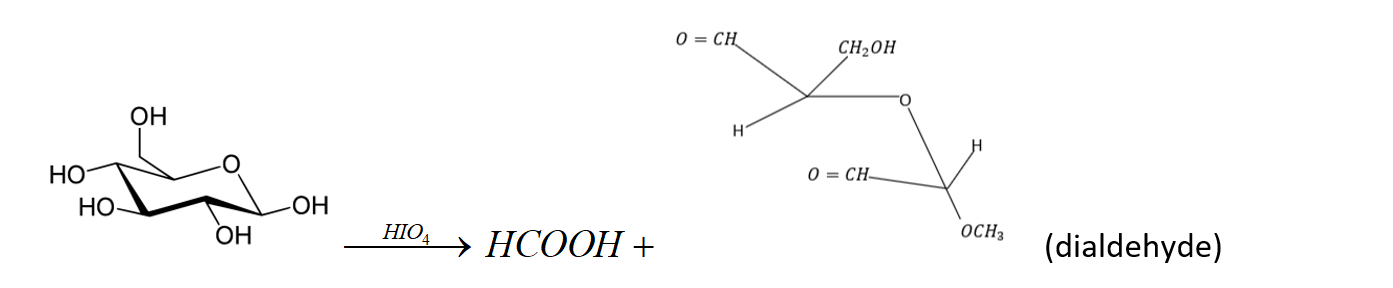
Note:
Chiral carbon: Those carbons whose all the four valencies are filled by different atoms or molecules. D- and L- configuration are different. It is based on the position of the hydroxyl group present in the carbohydrate.
