Question
Question: Metamers include _________ class of compounds. A.Functional B.Different C.Same D.None of th...
Metamers include _________ class of compounds.
A.Functional
B.Different
C.Same
D.None of the above
Solution
Isomers in chemistry are molecules or polyatomic ions that have the same molecular formula — that is, the same number of atoms of each element — but different atomic configurations in space. Isomerism refers to the existence or potential of isomers. Isomers don't always have the same chemical or physical characteristics as one another. Structural or constitutional isomerism, in which the bonds between the atoms differ, and stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism, in which the bonds are the same but the relative locations of the atoms differ, are the two primary types of isomerism.
Complete answer:
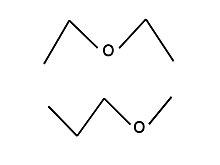
Metamers are isomers with identical molecular formulas but distinct alkyl groups on both sides of functional groups. Metamerism is the name given to this isomerism occurrence.
Diethyl ether and methyl propyl ether are two examples of ethers. Diethyl ether and methyl propyl ether have the same structural formula. C4H10O has the same chemical formula for both. The ether functional groups are present in both diethyl ether and methyl propyl ether. ROR is the general formula for ethers.
Two R groups equal two ethyl groups in diethyl ether. One R group in methyl propyl ether is methyl, and the other R group is propyl. The groups methyl, ethyl, and propyl can be represented as CH3, CH3CH2, !! !! CH3CH2CH2.
A kind of structural isomerism is metamerism. Metamers have the same molecular formula and functional group. Metamers, on the other hand, have distinct structural formulae.
Hence option C is correct.
Note:
The chemical attribute of having the same percentage of atomic components in various configurations in chemistry (obsolete, replaced with isomer). Metamers are compounds with the same chemical formula but variable numbers of carbon atoms (alkyl groups) on each side of a functional group (e.g., -O-, -S-, -NH-, -C(=O)-, esters, amides, etc.) in organic chemistry.
