Question
Question: Match list-I (complexes) with list-II (Hybridization of central atom) and select the correct answer ...
Match list-I (complexes) with list-II (Hybridization of central atom) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
| List-I | List-II |
|---|---|
| A. Ni(CO)4 | 1. sp3 |
| B. Ni(CN)42− | 2. dsp2 |
| C. Fe(CN)64− | 3. sp3d2 |
| D. MnF64− | 4. d2sp3 |
| 5. sp2d... |
A. A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
B. A-5, B-2, C-4, D-3
C. A-5, B-3, C-2, D-4
D. A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
Solution
Hint As we know that hybridization is the process of producing a degenerated type of orbital by mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels. During hybridization, atomic orbitals are mixed and a new hybrid orbital is formed.
Complete Step by step solution:
- In Ni(CO)4, Ni atom is sp3 hybridised. And this will lead to a tetrahedral geometry. We can see the structure:
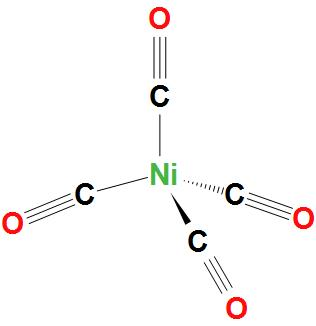
- In Ni(CN)42−, Ni atom is dsp2 hybridised. And this will lead to a square planar geometry.
Here, Ni(CN)42− is showing dsp2 hybridisation, because here CN group is a strong field ligand and it forms inner complexes. We can see the structure:
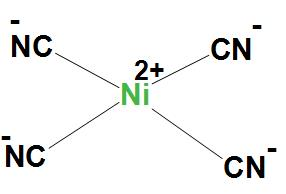
- In Fe(CN)64−, Ni atom is d2sp3 hybridised. And this will lead to an octahedral geometry. Here, Fe(CN)64− is showing d2sp3 hybridisation, because here cyanide group is present. And as we know that cyanide group is a strong field ligand and it forms inner complexes. We can see the structure:
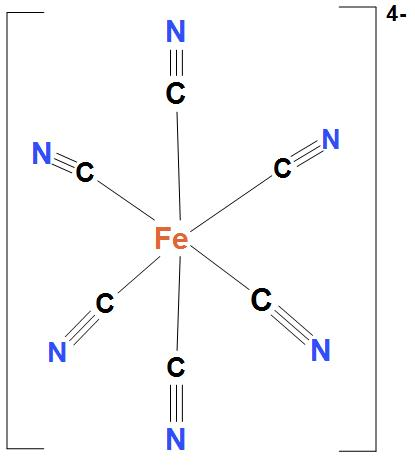
- In MnF64−, Ni atom is sp3d2 hybridised. And this will lead to an octahedral geometry. We can see the structure:
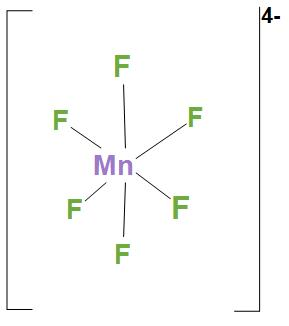
Hence, we can say that correct option is (d), that is A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
Note:
- We must note the key features of hybridization: the atomic orbitals that have equal energies undergo hybridization. Shape of any molecule can be predicted from hybridization.
- The number of hybrid orbitals that are formed during hybridization will be equal to the number of atomic orbitals mixed.
