Question
Question: Markovnikov’s rule for the addition of hydrogen halides to alkene states that the incoming hydrogen ...
Markovnikov’s rule for the addition of hydrogen halides to alkene states that the incoming hydrogen bonds to the:
A. sp2 carbon with the most hydrogens already
B. sp2 carbon with the fewest hydrogens already
C. sp3 carbon with the most hydrogens already
D. sp3 carbon with the few hydrogens already
Solution
Markovnikov’s rule for the addition of hydrogen halide to an asymmetric alkene. The addition of reagent takes place across the double bond. Markovnikov’s addition of hydrogen gives rise to a more stable carbocation.
Complete answer:
The addition of an asymmetric reagent to an asymmetric alkene takes place using Markovnikov’s rule.
Markovnikov’s rule states that when hydrogen halide is added to asymmetric alkene the acidic hydrogen gets added to less substituted carbon or carbon having more number of hydrogen atoms. While negative, the reagent gets added to the more substituted carbon atom of C = C the double bond. In the case of hydrogen halides, the negative part of the reagent is a halide. A more substituted carbon atom of C = C the double bond is the carbon which has less number of hydrogen atoms.
Consider the general reaction,
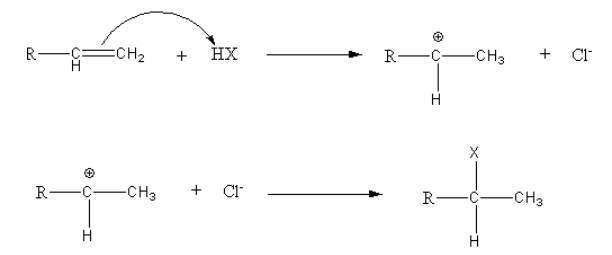
Thus, Markovnikov’s rule for the addition of hydrogen halides to alkene states that the incoming hydrogen bonds to the sp2 carbon with the most hydrogens already.
**Thus, the correct option is (A) sp2 carbon with the most hydrogens already.
Note:**
The first step of Markovnikov’s addition is the protonation of sp2 carbon with the most hydrogen already. This addition gives rise to more stable carbocation while protonation of sp2 carbon with the least hydrogens already gives rise to the least stable carbocation that is not favourable.
