Question
Question: Magnification equals \[-(\dfrac{v}{u})\]. Why is there a minus sign?...
Magnification equals −(uv). Why is there a minus sign?
Solution
The position and the size of the image are obtained by using lens formula and also by using magnification formula. The focal length is a measure of how strongly the system can converge or diverge rays of light and the focal length of concave lens and convex lens are different. The focal length is half of the radius of curvature in the case of a mirror. Refractive index of water is 1.333 and the refractive index of glass is 1.003.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Lens formula which gives a relationship between object distance, image distance and focal length. If the focal length is positive then the system will converge rays of light and if it is negative then the system will diverge rays of light.
Apparent depth is defined as the depth of an object which is in a denser medium as seen from the rarer medium.
A person with clear vision can see objects clearly at distances ranging from 25cm to essentially to infinity
The process of enlarging the apparent size of something is called magnification.
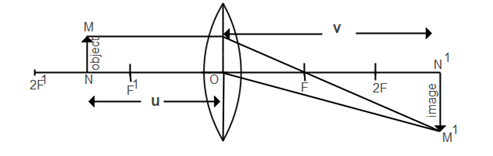
Magnification (M) is defined as the ratio of height of image(v) to the height of object(u). Which you can observe in the above diagram.
From the data Magnification formula is given by:
M=−uv
Minus sign indicates the type of image formed and the image is inverted
Minus sign resembles the real and inverted image formation after reflection on the screen.
Note: Students the polarity of focal length is negative for concave lens and it is positive for convex lens. Concave lens always forms a virtual and erect image while the convex lens forms a real and inverted image. By using lens maker formula we can build a lens with required focal length and there is standard value for focal length.
