Question
Question: Look at the indicator diagram and answer the following questions: (i) Which thermodynamic process ...
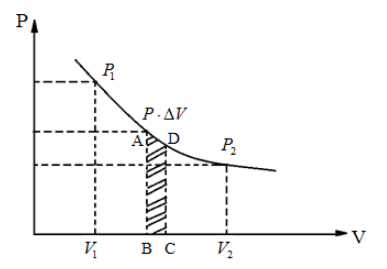
Look at the indicator diagram and answer the following questions:
(i) Which thermodynamic process does it possibly represent?
(ii) How much work is done when the volume of the working substance changes from V1 to V2?
Solution
In this question, we need to comment on the thermodynamic process involved in the given figure and evaluate the work done when the volume of the working substance changes from V1 to V2. For this, we will observe the given plot carefully and try to relate the different thermodynamic process with the given figure.
Complete step by step answer:
The graph of two variables x and y will be a rectangular hyperbola if the product x.y is always constant. It is known that the temperature is constant in an isothermal thermodynamic process.
In the above figure, the graph plotted between the pressure P and the volume V is in hyperbolic nature. Which means, the product P.V is constant. From the formula P.V=nRT, we can say that the right hand side of the equation, nRT is constant as the left hand side is also a constant. As the number of moles n and the universal gas constant R which is equal to 8.314J/mol are both constants, it can be said that the temperature T is also constant. Hence, the above indicator diagram represents an isothermal thermodynamic process.
Consider that in an isothermal process, the pressure and volume of the ideal gas changes from (P1,V1) to (P2,V2) . Somewhere in the middle of the process where the pressure is P and volume changes from V to V+ΔV, ΔV being infinitesimally small. From the first law of thermodynamics ΔW=PΔV, ΔV→0 as it is infinitesimally small and summing ΔW over entire process, we get total work done by the gas as
W=V1∫V2PdV where limits of integration goes from V1 to V2. Using the formula PV=nRT, we get P=VnRT
⇒W=V1∫V2(VnRT)dV
On integrating the above equation, we get
W=nRTln(V1V2) and as we know that ln=loge, this can be written as
W=2.303nRTlog(V1V2)
Note: The formula PV=nRT is used where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the universal gas constant and T is the temperature. First law of thermodynamics: ΔW=PΔV where ΔW is the change in work done, P is the pressure and ΔV is the change in volume. The work done can also be expressed in terms of initial pressure P1 and final pressure P2 as W=2.303nRTlog(P2P1).
