Question
Question: Look at the given heating curve for a pure substance carefully what is the physical state of the sub...
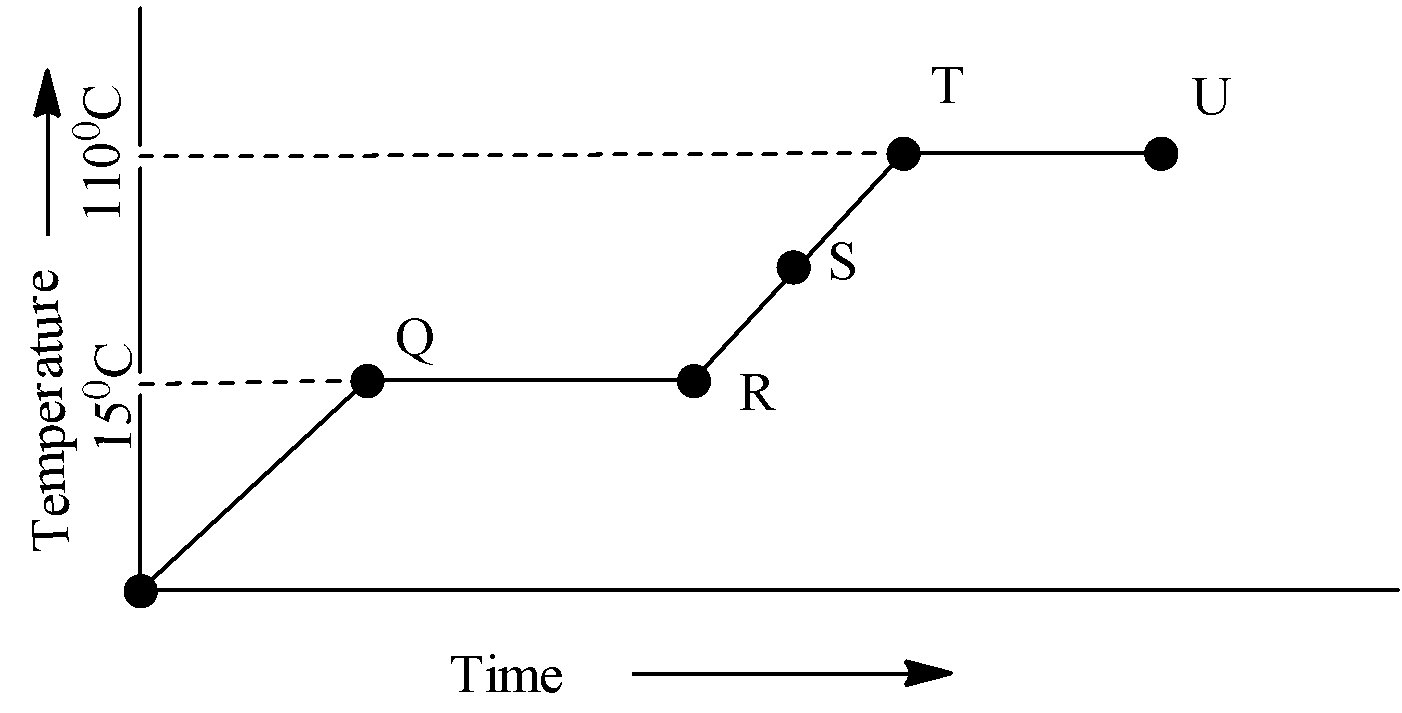
Look at the given heating curve for a pure substance carefully what is the physical state of the substance at point S?
(A) Solid
(B) Gas
(C) Liquid
(D) Liquid and gas
Solution
Hint if a given mass of a solid, heat is supplied to a constant rate and a graph is plotted between temperature and time shown in above diagram this graph is known as heating curve.
Complete Step by step answer:
In the region PQ rate of heat supply is constant and temperature of solid is changing with time. So rate of heat supply Q=mcs△Twhere, csrepresent the specific heat of solid csαslopeoflinePQ1
In the region QR temperature is constant so it represents the change in the physical state of the solid, melting of solid into liquid. Point Q is the melting point and point R all the solid is changed into liquid. So in between point P and Q substance is partially solid and partially liquid. This constant supplied heat is called latent heat of fusion. So supplied heat Q=mLf
Where Lfis the coefficient of latent heat of the fusion. {{\text{L}}_{\text{f}}}$$$\alpha $ Length of line QR Specific heat $\alpha $$$\dfrac{1}{\tan \,\theta }\,\,=\,\infty
In the region RT temperature of the liquid is increasing, so specific heat (thermal conductivity) of the liquid will be inversely proportional to the slope of the line RT cLαslopeoflineRT1
So, point ‘S’ lies in between the point between RT so, point ‘S’ represents the liquid state of the substance.
In the region TU temperature is constant, so changes in the physical state takes place. Liquid states of substance start boiling at point T and, at point U all the liquid will change completely in the vapor state.
Specific heat αtan,θ1,,=,∞
So, option (C) will be the correct answer.
Note: It is concluded from the above graph that the melting point of the substance is 15∘C and the boiling point of the substance is 110∘C. The slope of the graph is decreasing from solid state of substance toward vapor state of liquid (P to T). So, (specific heat capacity) solid >(specific heat capacity) liquid >(specific heat capacity) gas.
