Question
Question: List-I contains reaction and List-II contains major products. Match each reaction in List-I with o...
List-I contains reaction and List-II contains major products.
Match each reaction in List-I with one or more products in List-II and choose the correct option.
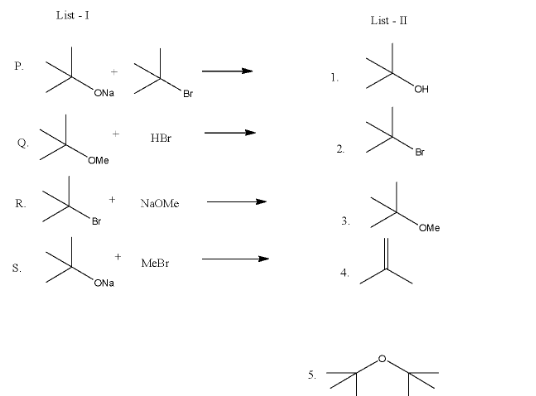
(a)- P→ 1, 5; Q → 2; R → 3; S → 4
(b)- P→ 1, 4; Q → 2; R → 4; S → 3
(c)- P→ 1, 4; Q → 1, 2; R → 3; S → 4
(d)- P→ 4, 5; Q → 4; R → 4; S → 3, 4
Solution
If the reactants contain bulky bases, then the reaction will be E2 an elimination reaction in which an alkene will be formed and if the base is not bulky, then there will be a substitution reaction.
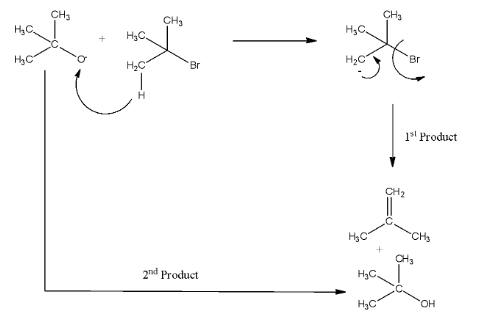
Complete answer: In reaction P, the two reactants are sodium tertiary butoxide and tert butyl bromide. The sodium tertiary butoxide is a bulky base, so it will attack the carbon atom that has the least steric hindrance. So, it will attack the acidic hydrogen from tertiary butyl bromide and E2 a reaction will occur. Now, there will be a negative charge on the carbon atom, and this will release the bromine and will form alkene as one product and alcohol. The reaction is given below:
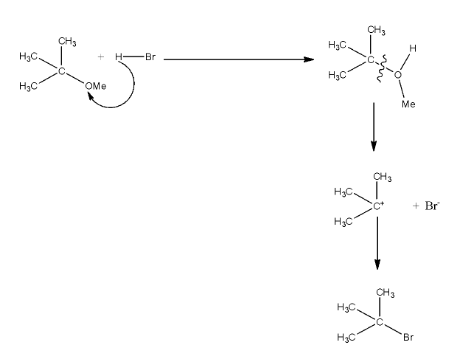
In Q, the reactants are ether and HBr, the hydrogen ion of the HBr will attack the ether. Now, the tertiary group will be released forming a carbocation, on this carbocation, the bromide ion will attack, and for tertiary butyl bromide. The reaction is given below:
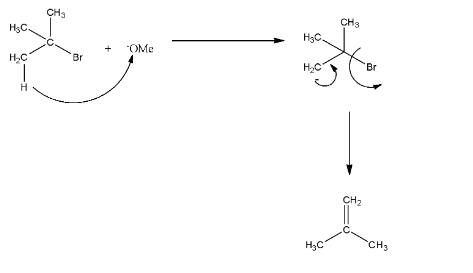
In R, the base is methoxide, so it will attack the acidic hydrogen from tertiary butyl bromide and E2 reaction will occur. Now, there will be a negative charge on the carbon atom, and this will release the bromine and will form an alkene. The reaction is given below:
In S, the base is bulky but the MeBr is a small group due to which elimination will not occur instead the Sodium will be substituted with the methyl group. The reaction is given below:
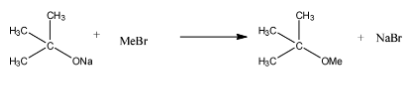
Therefore, the correct answer is option (b)- P→ 1, 4; Q → 2; R → 4; S → 3.
Note: In Q, the bond of Carbon and tertiary carbocation breaks instead of the bond between carbon and methyl because tertiary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation.
