Question
Question: Lines \[{{L}_{1}}:\dfrac{x-6}{3}=\dfrac{y-4}{2}=z-2\] and \[{{L}_{2}}:\dfrac{x-8}{4}=y-2=\dfrac{z-4}...
Lines L1:3x−6=2y−4=z−2 and L2:4x−8=y−2=2z−4 meets plane π:r⋅(2i+j−k)=7at points A,B then find area of triangle formed by the lines L1,L2 and AB is :
A). 27219
B). 219
C). 411
D). 65
Solution
First of all assume the point of intersection of both the lines be λ and μafter that find out the value of λ and μ by equating the equations, then find out the value of plane of line by applying vector dot product and we can find out the point of intersection of A and B then find out the area of triangle and check which option is correct in the above given options.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We have given two lines:
⇒L1:3x−6=2y−4=z−2 mark it as equation (1)
⇒L2:4x−8=y−2=2z−4 mark it as equation (2)
Let the point of intersection for equation (1)be λ
Now according to equation (1) we will find out the values of x,y,z
⇒3x−6=λ
⇒x−6=3λ
⇒x=3λ+6 mark it as equation (3)
Similarly find out the value of y
⇒2y−4=λ
⇒y−4=2λ
⇒y=2λ+4 mark it as equation (4)
Now find the value of z
⇒z−2=λ
⇒z=λ+2 mark it as equation (5)
Let the point of intersection for equation (2)be μ
Now according to equation (2) we will find out the values of x,y,z
⇒4x−8=μ
⇒x−8=4μ
⇒x=4μ+8 mark it as equation (6)
Similarly find out the value of y
⇒y−2=μ
⇒y=μ+2 mark it as equation (7)
Now find the value of z
⇒2z−4=μ
⇒z−4=2μ
⇒z=2μ+4 mark it as equation (8)
Equating the equation (3) and (6) we get:
⇒3λ+6=4μ+8
⇒3λ−4μ=8−6
⇒3λ−4μ=2 mark it as equation (9)
Equating the equation (4) and (7) we get:
⇒2λ+4=μ+2
⇒2λ−μ=2−4
⇒2λ−μ=−2 mark it as equation (10)
Now to find the value of λ we will multiply equation (10) by 4 on both sides, then subtract it from equation (9) we will get:
⇒(2λ−μ)×4=−2×4
⇒8λ−4μ=−8
Now subtract equation (9) from it:
⇒8λ−4μ−(3λ−4μ)=−8−2
⇒8λ−4μ−3λ+4μ=−10
⇒5λ=−10
⇒λ=−510
⇒λ=−2
Hence the point of intersection will be C(0,0,0)
We have given π:r⋅(2i+j−k)=7
As we know that r=xi+yj+zk , put the value of r we get:
⇒xi+yj+zk⋅(2i+j−k)=7
Apply dot product:
⇒2x+y−z=7
We will find the intersection point for L1 by putting the values of x,y,z from equation (3),(4),(5)
⇒2x+y−z=7
⇒2(3λ+6)+2λ+4−(λ+2)=7
⇒6λ+12+2λ+4−λ−2=7
⇒7λ=−7
⇒λ=−1
Point A will be: (3λ+6,2λ+4,λ+2)
Put the value of λ we get:
⇒A(3,2,1)
We will find the intersection point for L2 by putting the values of x,y,z from equation (6),(7),(8)
⇒2x+y−z=7
⇒2(4μ+8)+μ+2−(2μ+4)=7
⇒8μ+16+μ+2−2μ−4=7
⇒7μ=−7
⇒μ=−1
Point B will be: (4μ+8,μ+2,2μ+4)
Put the value of μ we get:
⇒B(4,1,2)
Hence to find the area of triangle will be:
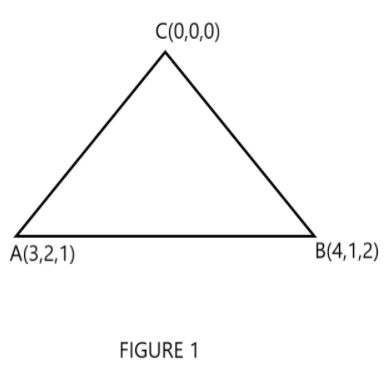
If we write it in vector form then:
⇒AC=3i+2j+k
⇒BC=4i+j+2k
⇒Area of triangle=21AC×BC
Now we will find the value of AC×BC
