Question
Question: Lindlar’s catalyst is: A. \(Pt\) in ethanol B. \(Pd+CaC{{O}_{3}}\) C. \(Ni\) in ethanol D. \...
Lindlar’s catalyst is:
A. Pt in ethanol
B. Pd+CaCO3
C. Ni in ethanol
D. Na in liquid NH3
Solution
Try to recall that Lindlar’s catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst which is used for the partial hydrogenation of alkynes. It gives cis-alkenes on reaction with alkynes. Now, by using this you can easily answer the given question.
Complete step by step answer:
- It is known to you that Pd+CaCO3 is known as Lindlar catalyst and is named after its inventor Herbert Lindlar Wilson.
- It is a heterogeneous catalyst which consists of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate with traces of lead and quinoline.
- Since, palladium is a good absorber of hydrogen and has very high catalytic properties. Therefore, it is poisoned with various forms of lead or sulphur or quinoline in order to reduce its activity of reducing double bonds.
- So, Pd+CaCO3 is used for the partial hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes and does not have the ability to reduce double bonds.
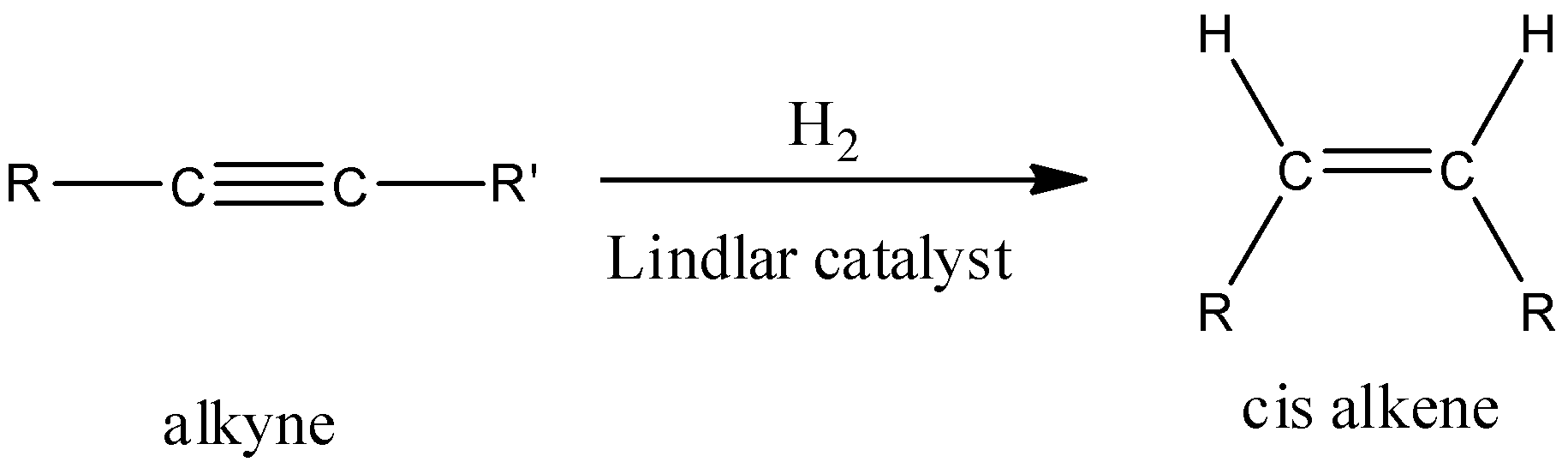
- Also, the product formed by using Lindlar’s catalyst i.e. Pd+CaCO3 is a cis-alkene.
- In the hydrogenation reaction of alkynes in presence of Pd+CaCO3, hydrogen atoms get added to the same side (cis) of alkyne and form cis-alkenes through syn addition (addition of two substituents on the same side of alkyne or alkene).
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Note that Hydrogenation of alkynes in presence of Lindlar’s catalyst is stereoselective and happens through syn addition. Also, it should be remembered that if Pd+CaCO3 is directly used without being poisoned then it will hydrogenate alkynes directly to alkanes. That’s why quinoline is used as a catalytic poison to stop the reaction at alkene.
