Question
Question: Let \(R\) be the resultant of \(P\) and \(Q\) and if \(\left( {\dfrac{P}{3}} \right) = \left( {\dfra...
Let R be the resultant of P and Q and if (3P)=(7Q)=(5R), then the angle between P and R is?
A) cos−1(1411)
B) cos−1(−1411)
C) 32π
D) 65π
Solution
Here, in the question, we are given that R is the resultant of P and Q vector and we have to find the angle between the vector P and the vector R. We know the formula to find the magnitude of resultant vector, which is R=P2+Q2+2PQcosθ, here P, Q, R are the magnitude of vectors and θ is the angle between vector P, Q. As we can see, in the given question the relation between three vectors is given so by using this we can find the value of θ. There is an another relation, cosϕ=RP+Qcosθ where ϕ is the angle between resultant vector R and vector P . So, from here we can find the value of the angle between P and R.
Formula used:
R=P2+Q2+2PQcosθ
On squaring both sides, we get
R2=P2+Q2+2PQcosθ
cosϕ=RP+Qcosθ
Complete answer: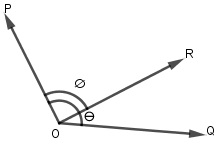
Given, 3P=7Q=5R
Let, λ=3P=7Q=5R
Or we can write it as,
⇒3P=λ,7Q=λ,5R=λ
⇒P=3λ,Q=7λ,R=5λ
We know that, R2=P2+Q2+2PQcosθ
Now, since we have values of P, Q and R we can substitute these values in the above written formula to get the value of cosθ.
⇒(5λ)2=(3λ)2+(7λ)2+2(3λ)(7λ)cosθ
On simplifying, we get
⇒25λ2=9λ2+49λ2+42λ2cosθ
Shift 9λ2 and 49λ2 to LHS,
⇒25λ2−9λ2−49λ2=42λ2cosθ
⇒−33λ2=42λ2cosθ
It can also be written as,
⇒42λ2cosθ=−33λ2
⇒cosθ=42λ2−33λ2
After cancelling out λ2 and division, we get
⇒cosθ=14−11
As we know that cosϕ=RP+Qcosθ.
Now, we will substitute the values of P, Q, R and cosθ in the above written formula.
⇒cosϕ=5λ3λ+7λ(14−11)
Take λ as a common factor
⇒cosϕ=5λλ(3+7(14−11))
On cancelling out λ, we get
⇒cosϕ=5(3+7(14−11))=53+(2−11)
⇒cosϕ=53−211
Solve the numerator by taking LCM
⇒cosϕ=526−11
⇒cosϕ=52−5
It can also be written as,
⇒cosϕ=2−5×51
⇒cosϕ=2−1
On shifting cos to RHS, we get
⇒ϕ=cos−1(2−1)
We know that, cos−1(−x)=π−cos−1x,x∈[−1,1]. Therefore, we get
⇒ϕ=π−cos−1(21)
We know that cos3π=21. So, on replacing, we get
⇒ϕ=π−cos−1(cos3π)
Also, we know cos−1(cosθ)=θ. Therefore, we get
⇒ϕ=π−3π
⇒ϕ=32π
Thus, the angle between P and R is 32π.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Note:
Here, in the given question we have found the value of angle between P and R using the formula cosϕ=RP+Qcosθ. If the question was about finding the value of the angle between Q and R we will not apply this formula. We will use cosϕ=RQ+Pcosθ. To solve these type of questions we should know all the required values of standard angles say,0∘, 30∘, 60∘, 90∘, 180∘, 270∘, 360∘ respectively for each trigonometric term such as sin, cos, tan, cot, sec, cosec, etc.
