Question
Question: Let \[f:\left[ { - \dfrac{1}{2},2} \right] \to R\] and \(g:\left[ { - \dfrac{1}{2},2} \right] \to R\...
Let f:[−21,2]→R and g:[−21,2]→R be function defined by f(x)=[x2−3] and g(x)=∣x∣f(x)+∣4x−7∣f(x), where []denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to y∈R. Then
(A) f is discontinuous at three point in [−21,2]
(B) f is discontinuous at four point in [−21,2]
(C) g is NOT differentiable exactly at four point in (−21,2)
(D) g is NOT differentiable exactly at five point in (−21,2)
Solution
First we find point of discontinuity of f(x)=[x2−3] by making graph. As we see that given function is a greatest integer function so it define only at integer point.
Next from the point of discontinuity of f(x) we define the function g(x)=∣x∣f(x)+∣4x−7∣f(x),
And find a point where it is not differentiable.
Complete step by step answer:
Given f(x)=[x2−3] is a greatest integer function and define in −21⩽x⩽2
Now we find x2−3 is define where
from the value of x
we say that 0⩽x2⩽4
now subtract 3 from above given equation
⇒−3⩽x2−3⩽1
Now take a greatest integer
⇒−3⩽[x2−3]⩽1
From this we can say f(x) take value from [−3,1] only at integer value.
f(x)=−3,,−2,−1,0,1
Now
1.f(x)=−3
Then [x2−3]=−3
So −3⩽x2−3⩽−2
⇒0⩽x2⩽1
From here −1⩽x⩽1
2. f(x)=−2
Then [x2−3]=−2
So −2⩽x2−3⩽−1
⇒1⩽x2⩽2
Now we take square root to find x
From here 1⩽x⩽2
3. f(x)=−1
Then [x2−3]=−1
So −1⩽x2−3⩽0
⇒2⩽x2⩽3
Now we take square root to find x
From here 2⩽x⩽3
4. f(x)=0
Then [x2−3]=0
So 0⩽x2−3⩽1
⇒3⩽x2⩽4
Now we take square root to find x
From here 3⩽x⩽2
5f(x)=1
Then [x2−3]=1
So 1⩽x2−3⩽2
⇒4⩽x2⩽5
Now we take the square root to find x
From here 2⩽x⩽5 but we know that function can not take value more than 2
So x=2
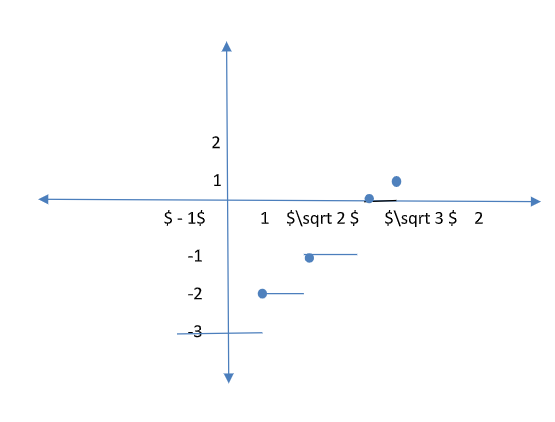
So from this, we can say it is discontinuous at 4 points.
Point of discontinuity \left\\{ {1,\sqrt 2 ,\sqrt 3 ,2,} \right\\}
So option B is the correct answer.
Now for function g(x)=∣x∣f(x)+∣4x−7∣f(x),
By putting value of f(x)
So first when −1⩽x<1 here f(x)=−3
So g(x)=−3∣x∣−3∣4x−7∣
When −1⩽x<0 then g(x)=3x+3(4x−7)
g(x)=15x−21
And when 0⩽x<1
In this ∣4x−7∣ open with negative sign
So g(x)=−3x+3(4x−7)
g(x)=9x−21
2. when 1⩽x<2; f(x)=−2
So g(x)=−2∣x∣−2∣4x−7∣
In this ∣4x−7∣ open with negative sign
so g(x)=−2x+2(4x−7)
g(x)=6x−14
3. when 2⩽x<3; f(x)=−1
So g(x)=−∣x∣−∣4x+7∣
In this ∣4x−7∣ open with negative sign
so g(x)=3x−7
4. When 3⩽x<2; f(x)=0
So g(x)=0.
5. when x=2;f(x)=1
So g(x)=∣x∣+∣4x−7∣
g(x)=5x−7
Now we have to find differentiability of g(x)
(i) At x=0
Right hand derivative g′(a+)=h→0limhf(a+h)−f(a)
So g′(0+)=h→0limhf(0+h)−f(0)
g′(0+)=h→0limh9h−21+21
So g′(0+)=h→0limh9h=9.
So right hand derivative = 9
Now left hand derivative
g′(a−)=h→0lim−hf(a−h)−f(a)
So g′(0−)=h→0lim−hf(0−h)−f(0)
g′(0−)=h→0lim−h15h−21+21
g′(0−)=h→0lim−h15h=−15
So left hand limit is not equal to right hand limit so function g(x) is not deprivable at x=0
(ii). At x=1
Left hand derivative
g′(1−)=h→0lim−hf(1−h)−f(1)
g′(1−)=h→0lim−h9(1−h)−21−6+14
g′(1−)=h→0lim−h−9h−4
By using L’HOSPITAL RULE
g′(1−)=h→0lim−1−9=9
And right hand limit.
g′(1+)=h→0limhf(1+h)−f(1)=h→olim−h6−6h−14−6+14=6
So left and write hand derivative are different so at x=1 it is not derivative
So by definition we can say if f(x) is not continuous and g(x)is a function of f(x) in this case g(x) is also discontinuous at these points. And if a function is not continuous at any point so the function is not derivable at these point
So 2,3 are point of discontinuity of g(x) that mean it is not derivable at these point also
We know that f(x) is discontinuous at x=2 but we can not include because queation ask point of not differentiability in between (−21,2)
So g is NOT differentiable exactly at four point in (−21,2)
Point where g(x) is not differentiable is
x=0,1,2,3
Therefore, option (B) and (C) are correct.
Note:
The differentiability of a function can be found by making a graph.
And differentiability of a function at the boundary point can be found by using one hand derivative either left or right hand.
