Question
Question: Let \[f\] be an odd function defined on the set of real numbers such that for \[x \geqslant 0\], \[f...
Let f be an odd function defined on the set of real numbers such that for x⩾0, f(x)=3sinx+4cosx. Then f(x) at x=6−11π is equal to
A. 2−3−23
B. 23−23
C. 23+23
D. 2−3+23
Solution
Here we use the concept of odd functions which is f(−x)=−f(x) and solve for the value at given x. We break the angle in such a way that it is added or subtracted from 2π.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have f(x)=3sinx+4cosx
Also, we know any function is an odd function if it satisfies f(−x)=−f(x).
Now we have to find the value of the function at point x=6−11π
We have to find the value of f(6−11π)
Since, f is an odd function, therefore, we can use the concept f(−x)=−f(x). Substitute x=6−11π.
⇒f(6−11π)=−f(611π)
Now we can break the angle inside the function as
⇒611π=612π−π
Separating the fraction into two parts
⇒611π=612π−6π
Cancel out common factors from numerator and denominator
⇒611π=2π−6π
Therefore, we can write
f(6−11π)=−f(2π−6π)
Now we know f(x)=3sinx+4cosx
Put x=2π−6π
⇒f(611π)=3sin(2π−6π)+4cos(2π−6π) … (1)
Now we will use the quadrant graph to convert the angles.
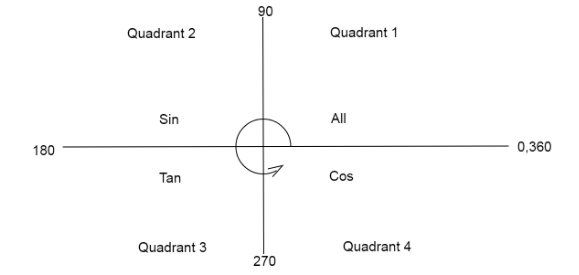
Here we denote 2π=360∘,π=180∘
Now we calculate the values of both the functions on RHS of the equation using the quadrant diagram.
For sin(2π−6π), we are subtracting from 2πwhich goes into the fourth quadrant where sin function is negative.
So, the value of sin(2π−6π)=−sin(6π)=−21 … (2)
For cos(2π−6π), we are subtracting from 2πwhich goes into the fourth quadrant where the cos function is positive.
So, the value of cos(2π−6π)=cos(6π)=23 … (3)
Substitute the values from equation (2) and equation (3) in equation (1)
⇒f(x)=3(2−1)+4(23)
Multiply the terms in the bracket.
So now f(−611π)=−f(611π)
Therefore,
So, option B is correct.
Note: Students are likely to make mistakes while calculating the values from the quadrant diagram, keep in mind that we always move anti-clockwise as we add the angles, so when we subtract the angle we move backwards or clockwise to see which quadrant our function lies in.
