Question
Question: Let \( \cos (\alpha + \beta ) = \) \( \dfrac{4}{5} \) and let \( \sin (\alpha - \beta ) = \) \( \dfr...
Let cos(α+β)= 54 and let sin(α−β)= 135 , where 0 ≤ α, β ≤ 4π , then tan2α is equal to
A. 720
B. 1625
C. 3356
D. 1219
Solution
Hint : We know the cosine of any angle is the ratio of the base to hypotenuse in a right angled triangle. Similarly, sine of any angle is the ratio of the opposite side to hypotenuse in a right angled triangle. Further, we will use Pythagoras theorem to calculate the other trigonometry ratio which is tan2α .
Formula Used: The following formula is used to get to the final answer,
tan(α+β)= 1−tanαtanβtanα+tanβ
Complete step-by-step answer :
According to the given information, we have
The first function is cos(α+β)= 54
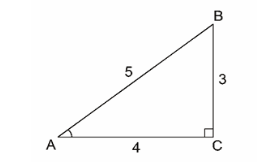
Also, we know cos(α+β)=54
Therefore take the base to be 4k and hypotenuse as 5k, where k is a constant.
Further, perpendicular = (hypotenuse)2− (base)2
⇒(5k)2−(4k)2 =9k2
Finally we get the perpendicular to be 3k.
Now for a right angled triangle ABC we know that,
tan(α+β)= 43 ...(1)
The second function is sin(α−β)= 135
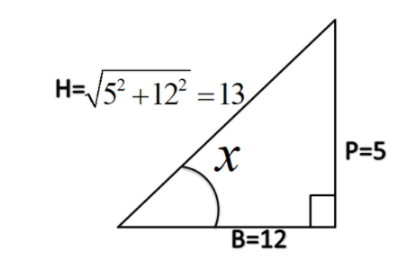
Also, we know sin(α−β)=135
Therefore, take the perpendicular to be 5k and hypotenuse as 13k, where k is a constant.
Further, base = (hypotenuse)2− (perpendicular)2
⇒(13k)2−(5k)2 =144k2
Finally we get the base to be 12k.
Now for a right angled triangle ABC we know that,
Hence we get,
tan(α−β)= 125 ...(2)
According to the given data,
The following formula is used to get,
tan(α+β)= 1−tanαtanβtanα+tanβ
tan((α+β)+(α−β)) = 1−tan(α+β)tan(α−β)tan(α+β)+tan(α−β)
On simplifying further we get,
tan2α =1−43×12543+125
⇒4848−154836+20 =3356
So, the correct answer is “3356 ”.
Note : In order to solve problems of this type the key is to have a basic understanding of trigonometric equations and values and also learn its implications. Students should be aware of applications of the trigonometric values in order to simplify the given equation.
