Question
Question: Let ABCD is parallelogram such that \[\overline {AB} = \overrightarrow q ,\overline {AD} = \overrigh...
Let ABCD is parallelogram such that AB=q,AD=p and ∠BAD be an acute angle. If r is the vector coincides with the altitude directed from the vertex B to the side AD, then r is given by:
(A) r=3q−p.p3(p.q)p (B) r=−q+(p.pp.q)p (C) r=q−(p.pp.q)p (D) r=−3q+p.p3(p.q)pSolution
This problem is related to vector geometry. It should be noted here that a dot product of two vectors is a scalar quantity (A.B=ABcosθ, where θ is the angle between them) and if the vectors are perpendicular to each other their dot product is zero because the value of cos90∘=0. We will use this property of vector products to solve the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Firstly, draw a parallelogram ABCD in such a way that AB=q,AD=p and ∠BAD should be an acute angle. See below,
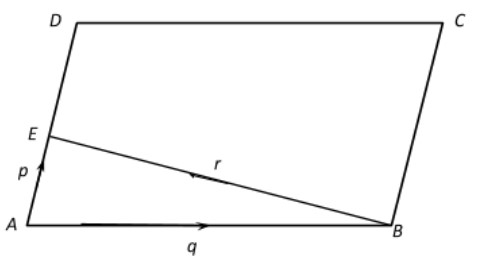
Now, in the diagram, draw a line originating from vertex B to the side AD in such a way that it should be perpendicular to side AD. This way ΔAEB will be a right angle triangle.
We know that, vectorrcan be written in the form of vector q and vector p. Now, from the diagram above, it is known that the direction of vector ris opposite to the direction of vectorq. Hence, when we write the vector r in terms of vector q, we shall have to put a negative sign in front of the vector q.
Now, vector prepresents the side AD, so assume that αprepresents the side AE in ΔAEB. Therefore, now vector rcan be written in the form of vector q and vector p in the following way,
r=−q+αp ................(1)
Now, we know that the dot product to two perpendicular vectors is zero. In this diagram, vectorrand vectorp are perpendicular to each other.
Therefore,
r.p=0
Putting the value of vectorr from eq. (1) in the above expression, we will get
Now, putting this value of α, we will get the value of vectorras
r=−q+p.pq.pp
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: In these types of problems, you should take care while drawing the diagram and putting the vector’s direction. Though, it is not given in the problem that the vector ris perpendicular topbut we have assumed that they are perpendicular to each other so that property of dot product of vectors can be utilised.
