Question
Question: Let ABC be a triangle in which AB = BC. Let X be a point on AB such that AX: XB = AB: XA. If AC = AX...
Let ABC be a triangle in which AB = BC. Let X be a point on AB such that AX: XB = AB: XA. If AC = AX, then the measure of ∠ABC equals?
A. 18∘ B. 36∘ C. 54∘ D. 72∘
Solution
Hint: In order to find the measure of ∠ABC we consider the given ratio from the question and rearrange it to express the side AX in terms of AB. Then we apply the formula of cos θ in the triangle ∆ABC and deduce the value of the required angle to get the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given Data,
AB = BC
AX: XB = AB: XA
AC = AX
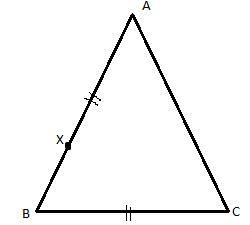
Given that AX: XB = AB: XA
⇒XBAX=AXAB ⇒XB + XAAX=AX + ABAB ⇒ABAX=AX + ABAB ⇒AX2+AX×AB = AB2
Now let us add the term (2AB)2on both sides to make it look like the formula of expansion of the form(a + b)2=a2+b2+2ab.
⇒AX2+ 2×AX×2AB + (2AB)2 = AB2+(2AB)2 ⇒(AX + 2AB)2=45(AB)2 ⇒AX = 25AB - 2AB - - - - - (1)
Now let the side of the triangle AB = a.
Given that AB = BC, therefore AB = BC = a
AC = AX = (25−1)a (From equation (1))
Now in the triangle ∆ABC,
We know,cos θ = hypotenuseadjacent
Therefore the measure of ∠ABC equals 36°.
Option B is the correct answer.
Note – In order to solve this type of problems the key is to know the concepts of ratios, angles in a triangle, trigonometric function definition of ‘cos’ and formulae for expansions of terms of the form (a + b)2.
We basically express AX in terms of AB using the given ratio and then express other sides in terms of AB using the relations given in the question. Once we find the lengths of sides expressed in the required form we apply the cos function to the triangle and solve for the answer.
We refer to the trigonometric table of cos function to find the value of the cos inverse function.
